Published December 2023
Acrylic acid and esters are versatile monomers used as building blocks for thousands of polymer formulations. They are flammable, reactive, volatile liquids based on an alpha-, beta-unsaturated carboxyl structure. Incorporation of varying percentages of acrylate monomers permits the production of many formulations for latex and solution copolymers, copolymer plastics and cross-linkable polymer systems. Their performance characteristics — which impart varying degrees of tackiness, durability, hardness and glass transition temperatures — promote consumption in many end-use applications. Major markets for the esters include surface coatings, textiles, adhesives and plastics. Polyacrylic acid or copolymers find applications in superabsorbents, detergents, dispersants, flocculants and thickeners. Superabsorbent polymers (SAPs) are used primarily in disposable diapers.
The following pie chart shows world consumption of acrylic acid:
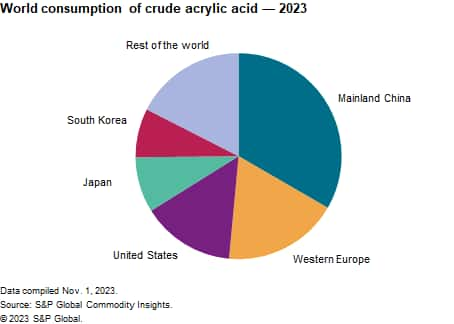
Crude acrylic acid (CAA) is made by the oxidation of propylene. About half of the CAA is converted to acrylate esters, and the remaining half is purified to 98%-99.5% purity to glacial acrylic acid (GAA). In turn, GAA is converted into polyacrylic acid, which can be further modified to produce superabsorbent polymers (SAPs) and other polyacrylic acid copolymers used as dispersants/antiscalants, anionic polyelectrolytes for water treatment and rheology modifiers. Growth in GAA consumption is forecast at about 3% per year during 2023–28.
Acrylate esters impart many desirable qualities to polymeric materials, such as color stability and clarity, heat and aging resistance, good weatherability and low-temperature flexibility. One of the important properties of acrylate esters is their glass transition temperature (Tg), which influences the characteristic temperature at which the resultant polymer undergoes a change from a brittle system to a softer, more flexible one. The Tg has a major influence on the minimum film formation temperature of the coating or adhesive. (The minimum film formation temperature is also influenced by the levels and types of cosolvents and coalescing agents, plasticizers, and other additives added to the polymer or to the coating formulation.) The shorter-chain monomers (e.g., methyl acrylate) produce harder, more brittle polymers, while the longer-chain monomers (e.g., 2-ethylhexyl acrylate) impart softness and flexibility.
Growth in demand for crude acrylic acid is forecast at 2.5%-3% per year during 2023–28, driven by growth in superabsorbent polymers and acrylate esters. SAP growth will be strongest in developing nations in Asia but will be much more moderate in mainland China as population growth moderates. Growth in the mature regions of North America, Western Europe and Japan will be continue to be slow.
SAP is being used in greater quantities as the population in developing nations continues to increase its use of disposable diapers and incontinence products. Acrylic esters are used principally in coatings and adhesives, which are also areas of growth in developing countries.
For more detailed information, see the table of contents, shown below.
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Acrylic Acid and Esters is the comprehensive and trusted guide for anyone seeking information on this industry. This latest report details global and regional information, including
Key benefits
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Acrylic Acid and Esters has been compiled using primary interviews with key suppliers and organizations, and leading representatives from the industry in combination with S&P Global’s unparalleled access to upstream and downstream market intelligence and expert insights into industry dynamics, trade and economics.
This report can help you
- Identify trends and driving forces influencing chemical markets
- Forecast and plan for future demand
- Understand the impact of competing materials
- Identify and evaluate potential customers and competitors
- Evaluate producers
- Track changing prices and trade movements
- Analyze the impact of feedstocks, regulations, and other factors on chemical profitability

















