Published October 2024
Acrylic fibers are synthetic fibers made from the polymer polyacrylonitrile (PAN), which contains at least 85% by weight of the monomer acrylonitrile. Modified acrylic fibers, in which the acrylonitrile monomer content is less than 85% but at least 35%, are referred to as modacrylic fibers. In modacrylic fibers, the remaining 15%-65% consists primarily of halogenated comonomers that impart a high degree of flame retardancy to the fibers. Acrylic staple fiber accounts for virtually 100% of the acrylic fiber produced. Continuous filament fiber is used mainly for conversion to carbon fibers.
Acrylic fibers are more suited than modacrylic for processing into high-bulk yarns. Fabrics produced from acrylic yarns are lightweight and resilient and generally have warmth and softness similar to wool. Acrylic fibers possess an aesthetic appeal enhanced by their ability to accept dyes of both clear, bright colors and subdued, muted tones. They have excellent resistance to ultraviolet degradation, microbiological attack, weak alkalis and laundry bleach.
During the past 10 years, acrylic fibers have progressively lost market share to polyester fibers. Entering 2020, supply and demand in almost every region was impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic. Even though recovery began in 2022, the global rebound has fallen short of expectations because of reduced demand from the textile and apparel industry in general, coupled with increasing competition from other fibers, particularly from polyester. Because of declining demand, the global acrylic fiber industry has undergone major restructurings and capacity rationalizations. Some old production facilities have been shut down or idled, and some manufacturers have converted acrylic fiber capacity to polyacrylonitrile (PAN) precursor capacity for carbon fiber production.
The following pie chart shows world consumption of acrylic fibers:
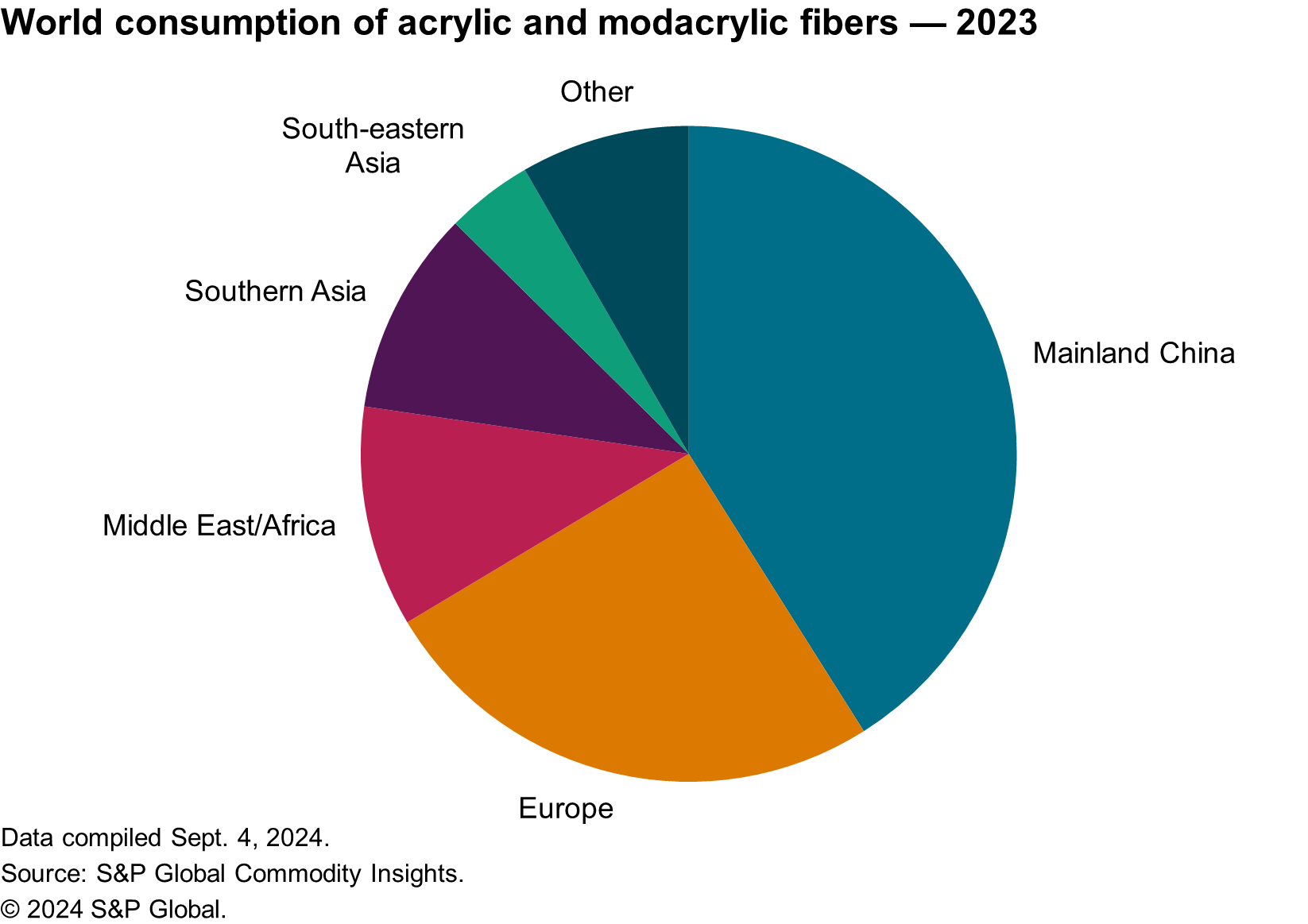
In 2023, Asia held the largest share of total capacity with mainland China as the largest single market. Although mainland China is still not self-sufficient in acrylic fiber supply, its imports have contracted significantly over the last decade. Mainland China shifted to being a net exporter of acrylic fibers in 2022, which has altered the trade flow patterns at the world level.
Asia remains the largest market for acrylic fibers, where demand is being driven by local textile mills producing apparel, the majority of which is exported worldwide. However, the market share has contracted over the last several years because of slow market recovery since the pandemic and the encroachment of alternative materials like polyester and viscose.
For more detailed information, see the table of contents, shown below.
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Acrylic and Modacrylic Fibers is the comprehensive and trusted guide for anyone seeking information on this industry. This latest report details global and regional information, including
Key benefits
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Acrylic and Modacrylic Fibers has been compiled using primary interviews with key suppliers and organizations, and leading representatives from the industry in combination with S&P Global’s unparalleled access to upstream and downstream market intelligence and expert insights into industry dynamics, trade, and economics.
This report can help you
- Identify trends and driving forces influencing chemical markets
- Forecast and plan for future demand
- Understand the impact of competing materials
- Identify and evaluate potential customers and competitors
- Evaluate producers
- Track changing prices and trade movements
- Analyze the impact of feedstocks, regulations and other factors on chemical profitability


















