Article: How are the environmental and regulatory challenges facing glyphosate impacting its global market and other non-selective herbicides?
According to latest research by Phillips McDougall published in the AgrAspire suite of interactive data explorers the global market for glyphosate totaled an estimated $5,325 million in 2018 representing a +4.2% increase over 2017.
Global Glyphosate Market ($m.)
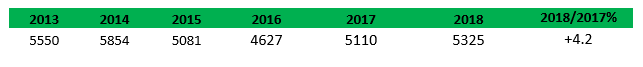
Glyphosate prices continued to rise in 2018, albeit at a reduced rate when compared to the approximate 25% increase between 2017/2016. A key driver in this continues to be the environmental crackdown on manufacturers in China, as well as governmental polices aimed at consolidating the Chinese market. This regulation also covers the phosphate supply market - a key intermediate in the production of glyphosate.
Indications of flat to moderately declining volume demand for the active in 2018 have only been moderately offset by price increases, albeit at a diminishing rate as the market seeks to re-equilibrate following regulatory concerns over the ai. This has benefitted the other major amino acid herbicide glufosinate, which is estimated to have increased by +22.1% in 2018 to reach $916 million in 2018.
Overall, the US saw a 5% decline in the volume of glyphosate used from 2017 to 2018 - prices increasing slightly by 8%; however there was some variance across different crop groups:

Global Glufosinate Market ($m.)

The global glufosinate market has been influenced in part by a pricing mix effect in relation to the recent rises in glyphosate prices. The increased cost of manufacture for glyphosate in China resulting from regulatory action has also had the effect of making glufosinate, which is more expensive to produce and thus a higher cost product, more competitive in the market. Issues surrounding glyphosate resistance and the uncertainty pertaining to the future regulatory system are also driving strong growth of glufosinate. The performance of the LibertyLink trait conferring tolerance to glufosinate has also contributed to growth in 2018, with the global total of all seeds containing the trait estimated to have risen by +17.2% to $1,361 million in 2018.
In the domestic China context, 2018 saw a big increase in the volume of glufosinate used across several crop groups:

In terms of other non-selective herbicides 2,4-D grew strongly during 2018, rising by +11.5% to reach $748 million. 2,4-D continues to perform well as an alternative to glyphosate in light of the above factors influencing the glyphosate market and following the continued market penetration of Enlist (glyphosate and 2,4-D) traits in cotton, and the initial US launch of Enlist maize during the 2018 planting season.
Global 2,4-D Market ($m.)

Additionally, the 2,4-D market benefitted from a recovery in the Brazilian inventory situation, particularly in the soybean sector as well as robust performance of the Asian cereal sector where increases in China and India offset a decline in the Australian cereal herbicide market following drought.
Dicamba has also performed well during the year, rising by an estimated +13.8% to reach $388 million, boosted by the continued strong performance of the Xtend trait system from legacy company Monsanto which was initially launched as Genuity Bollgard II XtendFlex cotton, followed by the 2016 launch of Roundup Ready 2 Xtend soybeans.
Dicamba Market ($m.)

XtendFlex provides tolerance to dicamba as well as glyphosate and glufosinate, which has been another positive factor in the 2018 performance of those ais.
Detailed market analysis of the performance of chemical classes and their constituent active ingredients can be found in the Product Section of Phillips McDougall AgriService report.
In terms of the regulatory situation and outlook for the ai, the latest situation according to IHS Markit's crop protection news service Agrow is:
For the last couple of years, glyphosate has been occupying centerstage in the US and the EU, albeit in different contexts. In the US, legal cases involving the herbicide have been regularly making headlines. In the EU, the regulatory uncertainty surrounding the active ingredient has caused a lot of debate.
In the US, there have been three judgments against Bayer. In August 2018, a California jury awarded a plaintiff $280 million, which a judge subsequently reduced to $80 million. In March 2019, a federal jury awarded $80 million, which a judge later reduced to $25 million. In a third case, a California jury awarded $2 billion to two plaintiffs. But that was reduced to $87 billion by a judge. Bayer is pursuing further appeals. Meanwhile, the US EPA again declared glyphosate as non-carcinogenic and has prohibited product labelling calling glyphosate carcinogenic. The EPA itself has been taken to court on its decision to re-register glyphosate.
In the EU, glyphosate was renewed for five years instead of the usual period of 15 years. Its renewal ends in December 2022. In the meantime, some member states, including Austria, France, Germany and Luxembourg, have announced their intention to completely phase out the herbicide.
This article was published by S&P Global Commodity Insights and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.