Global Power and Renewables Research Highlights, February 2022
Renewables costs and financing, US interconnection issues, hydrogen, and more
The following provides a brief overview of selected reports in the Global Power and Renewables service from January 2022. To learn more about IHS Markit's Global Power and Renewables Service and the reports featured in this post, click here.
January reports explored issues related to renewables costs, financing, and interconnection in addition to low-carbon hydrogen and transport decarbonization as growth opportunities for power and renewables as well as key questions facing Asian power markets in 2022.
Renewables costs, financing, and US interconnection
While recent pandemic-related supply chain disruptions have put pressure on renewable costs in many markets and access to low-cost financing remains a key challenge in Asia Pacific, decarbonization goals and new routes to market continue to drive renewables growth.
In North America, according to the IHS Markit Data "North America Solar PV Capital Cost and LCOE Outlook, January 2022", supply chain constraints and shipping delays are expected to raise the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) for solar photovoltaic (PV) in the near term, up to 10% in 2021-23, after which costs decline in the mid-2020s, driven by incremental technology improvements and scale, and reach new lows by the early 2030s despite the step down in the federal tax credit. According to the IHS Markit Data "North America Wind Capital Cost and LCOE Outlook, January 2022", onshore wind capital costs are also expected to increase 5% in 2022, owing to pandemic-related disruptions, although recent extensions of the production tax credit qualification window have mitigated significant impact on LCOE—with the looming tax credit phaseout likely to have a greater impact than the temporary capital cost increase. Meanwhile, offshore wind LCOE will continue to decline, driven mainly by reductions in capital costs and rising capacity factors, but costs will remain high.
In Asia Pacific, while 110 GW of solar PV and wind was added in 2020 alone—accounting for over half of the total installed capacity in the world—most Asian markets are expected to fall short of the US$125 billion of annual investment required to meet government renewables targets during 2021-25, with access to low-cost financing remaining one of the key challenges and new sources of finance needed to fill the gap. According to the IHS Markit Insight "The changing landscape of renewable energy financing in Asia Pacific", only mainland China is expected to meet the government's ambitions. In Vietnam, green loans are emerging as a new debt instrument for renewable projects, with the issuance of green loans in the country growing to US$1.7 billion since 2017. India also has significant potential to multiply renewables investment but needs to address policy, offtaker, and currency risks. Meanwhile, in Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan, the current offshore financing landscape signals a potential decrease in the perceived risk of capital providers in the near future, although the local industry's limited experience and localization requirements in South Korea and Taiwan may impede the sector's growth.
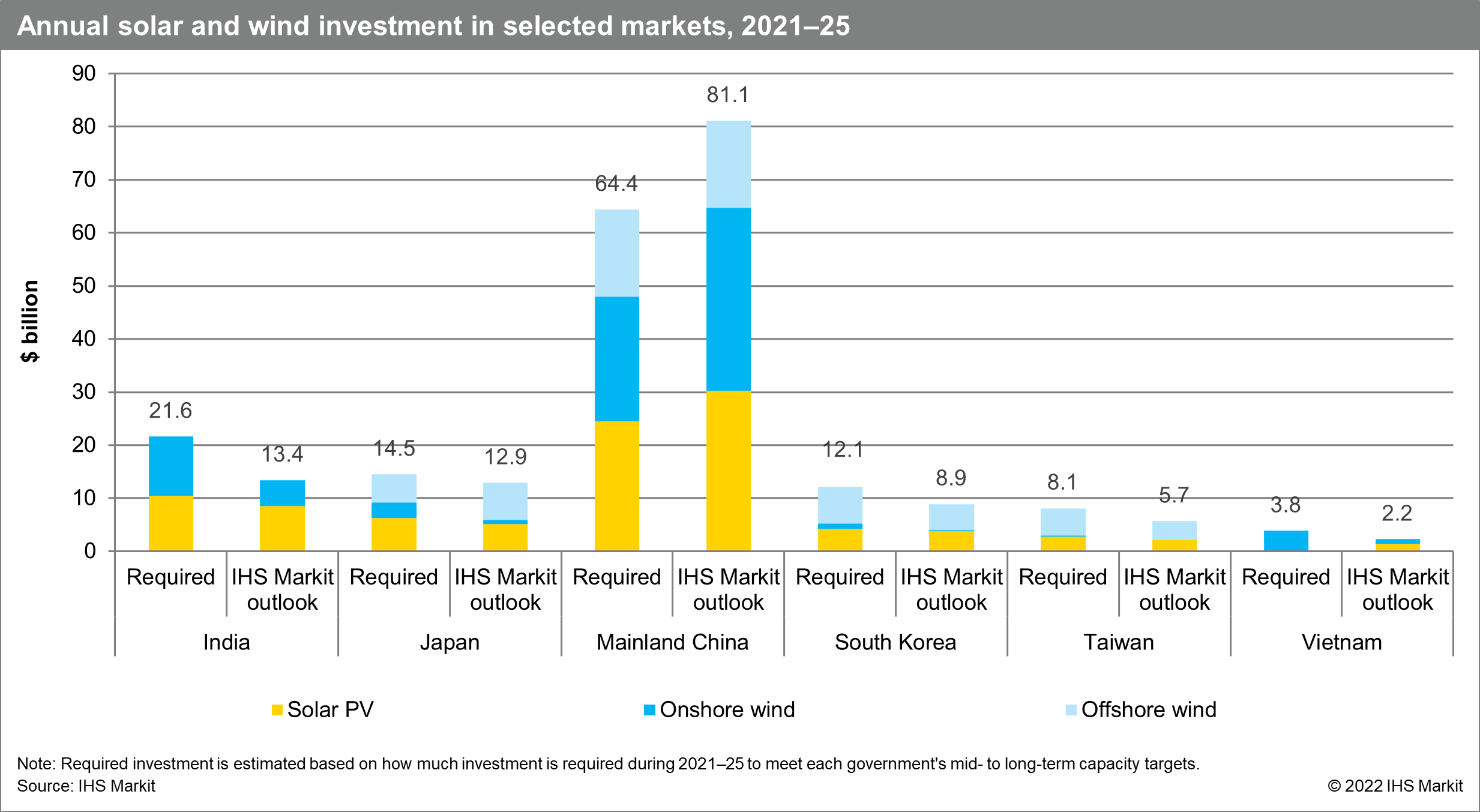
At the same time, according to the IHS Markit Insight "Green day-ahead market: A growing market segment for renewable capacity in India", since the October 2021 launch of India's green day-ahead market (GDAM)—a new market segment for trading day-ahead contracts for renewable generation—326 GWh of renewable energy has been traded, representing roughly 1.4% of total renewable energy generation and about 1.5% of the total short-term market. While prices continue to be divergent between the GDAM, the day-ahead market, and renewable energy certificates, liquidity in the GDAM is expected to increase, paving the way for implementation of other structural changes in the Indian power market.
Meanwhile in Europe, to date, the development of new wind and solar technologies has been mostly fueled by dedicated government support schemes. In recent years, however, a growing share of projects have been developed on a "market" basis without any direct government help, driven by declining generation costs and rising (or expectations of rising) spot prices, raising questions over whether subsidies remain necessary. The IHS Markit Insight "Can wholesale power markets alone deliver the 2030 renewable objectives?" finds that market forces alone, however, are unlikely to be sufficient to reach Europe's 2030 renewable objectives, with growing cannibalization and decreasing gas prices pushing the wholesale value of renewables below their LCOE and leading to a growing "missing money" gap for renewables despite decreasing costs.
According to IHS Markit Insight "Prospects of heightened competition in Europe's renewable market", in the coming years renewable developers in Europe will increasingly compete for the right sites and for materials and equipment to build assets while consumers will compete for supply as demand for green power increases, also spurred by green hydrogen targets. Local opposition will remain an important barrier while power purchase agreements (PPAs) will continue to grow despite transactional barriers, offering a second route to market, as corporate appetite for green power deepens. Indeed, according to the IHS Markit Scheduled Update "European corporate PPA market tracker: Record activity in fourth quarter 2021", 22.1 TWh was subscribed under a corporate PPA contract in Europe during 2021, representing a 50% volume increase year over year.
Swelling US interconnection queues increase costs
As renewables development continues to grow, interconnection queues and transmission infrastructure will need to keep pace to connect those resources, which tend to be farther away from load centers, to the grid.
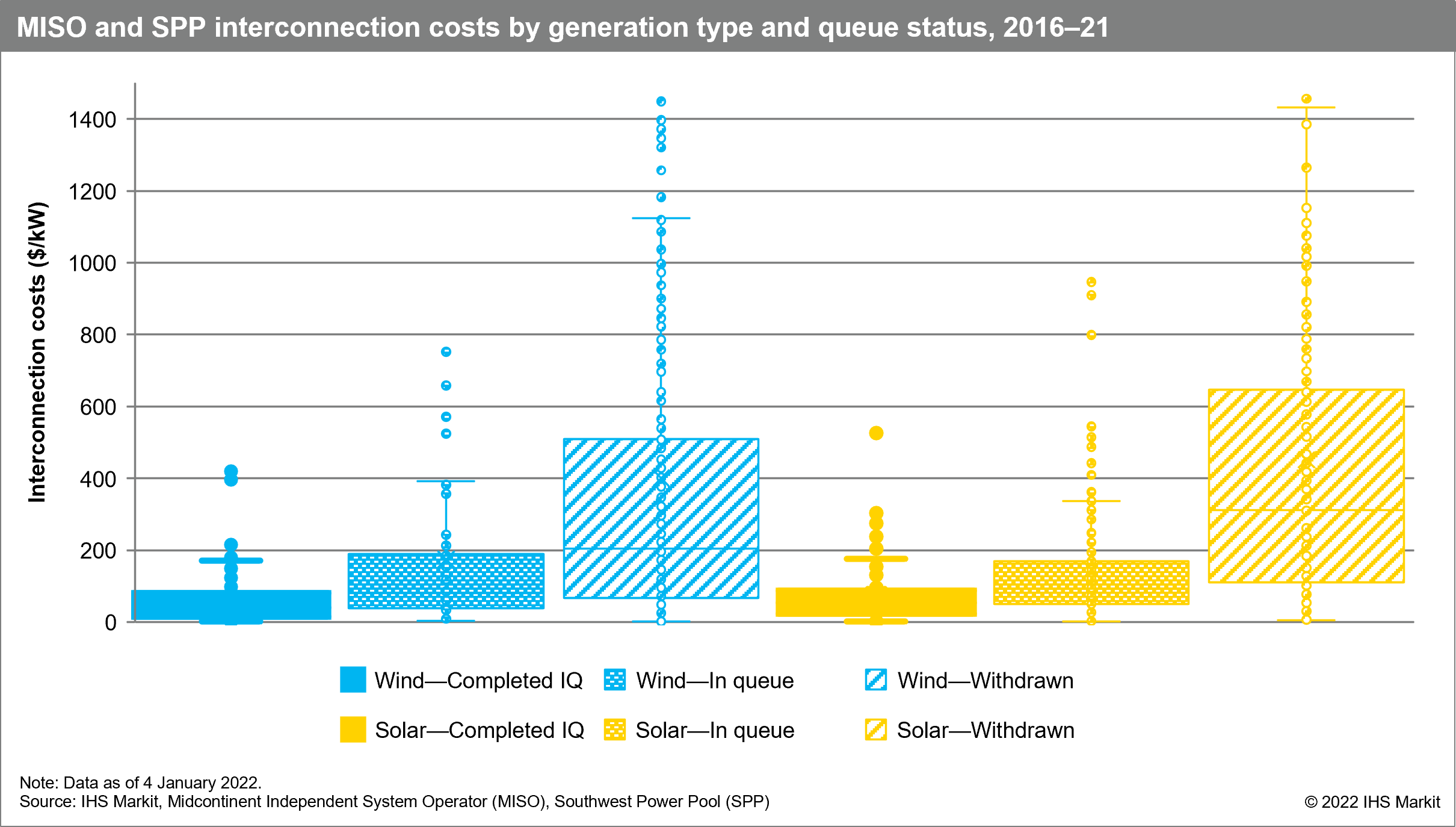
In many independent system operators across the United States, interconnection queues and study cycles are growing rapidly, leading to process delays and rising interconnection costs. According to the IHS Markit Insight "Interconnection woes across the Mid-Continent", the cost of interconnecting new generation in the Midcontinent Independent System Operator (MISO) and Southwest Power Pool (SPP) regions can vary extensively, in some cases increasing project capital costs to the point of economic infeasibility. While some wind and solar projects have interconnection costs greater than $1,000/kW, most projects that complete the queue process have interconnection costs less than $100/kW—still a significant cost that can increase a project's capital cost by upward of 10%. By contrast, interconnection costs for natural gas-fired projects are much lower since they are less affected by geographic location and have more flexibility on where to interconnect.
Hydrogen and transport decarbonization
As countries transition away from using carbon-intensive energy resources, low-carbon hydrogen is also expected to become an important energy source for difficult-to-electrify industries. In many of the largest markets, demand for low-carbon hydrogen is likely to exceed the local production capability, creating a market for low-carbon hydrogen imports and boosting renewable development.
According to the IHS Markit Insight "Canadian exports of low-carbon hydrogen could drive a new wave of renewable development", Canada is well positioned to be a competitive global supplier of low-carbon hydrogen. By 2050, nearly 100 TWh per year of additional low-carbon energy could be needed to support the annual production of 2.2 million metric tons (MMt) of green hydrogen exports, increasing baseline electricity demand in Canada by 16%, and spurring the development of 21 GW of onshore wind and 2 GW of offshore wind—representing 40% of Canada's total installed capacity of wind resources in 2050.
Latin America also aims to become a global supply hub for hydrogen and associated clean fuels, with Chile, Brazil, Argentina, and Colombia developing ambitious policy road maps for a future low-carbon hydrogen industry and gaining investor interest in response. The IHS Markit Insight "Latin America aims to be a global powerhouse for low-carbon hydrogen: Policy and industry developments in the region" explores policy and industry developments in the region, discussing the countries' challenges and opportunities to develop a hydrogen economy.
Transportation decarbonization is also becoming a major component of government policies striving to achieve mid-century net-zero carbon goals and represents a substantial growth opportunity for the power sector. According to the IHS Markit Strategic Report "Decarbonizing road transportation: A growth market for the US power industry", increases in battery electric vehicle (BEV) charging load and hydrogen electrolysis power demand (to make hydrogen for fuel cell electric vehicles) account for 70% of total US power demand growth between now and 2050. Under a Fast Transition case— which assumes US power sector and economywide carbon net neutrality by 2040 and 2050 respectively—the impact is even greater, with BEV charging load and electrolysis demand combining to provide 95% of power demand growth through 2050.
Big questions facing Asian power markets in 2022
As 2022 begins, IHS Markit is looking at key questions and anticipated trends in power and renewable markets this year. According to the IHS Markit Insight "A review of 2021 and the five big questions facing Southeast Asia's power markets in 2022", big questions facing Southeast Asia's power market in 2022 include post-pandemic power demand rebound, the energy transition and prospects for renewables, cross-border power transactions, and the role of international players in the region.
According to the IHS Markit Insight "Ten big questions for China's gas and power markets in 2022", key issues for China's power markets in 2022 also include post-COVID-19 economic growth, in addition to the potential for fuel supply disruptions and power rationing, China's national emissions trading scheme (which commenced in July 2021), price liberalization efforts and power spot market reform progress, the new "game rules" for renewable newbuilds in the post-grid parity era, and energy storage. The IHS Markit Insight "Five big questions facing OECD Asia's power market in 2022" explores key questions that will shape the discussions around power markets in Australia, Japan, and South Korea in 2022, including policies and implementation plans toward carbon neutrality, coal power generation, corporate PPAs and renewable energy growth, offshore wind, and new technologies such as hydrogen and carbon capture, utilization, and storage.
Stay tuned for additional key regional power market issues and an upcoming report summarizing anticipated trends in 2022 for global power and renewable markets.
Learn more about our global power and renewable research.
Rama Zakaria is associate director of Global Power and Renewables at IHS Markit.
Posted on 27 January 2022
This article was published by S&P Global Commodity Insights and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.