Global PV inverter market surpassed $9 billion in 2019 following record shipments
The PV inverter market achieved record shipments, growing by 19% to 126 GW in 2019 driven by booming shipments in key markets such as United States, Spain, Latin America, Ukraine and Vietnam. PV inverter revenue also increased rapidly, surpassing $9.1 billion in 2019 for the first time. Meanwhile, the global competitive landscape remains relatively consolidated. The top 10 suppliers accounted for over 70% of global PV inverter shipments. As the industry continues to enjoy rapid growth, competition is expected to continue to escalate among PV inverter suppliers due to two key factors: advancements in technology and the shifting balance of global installations growth.
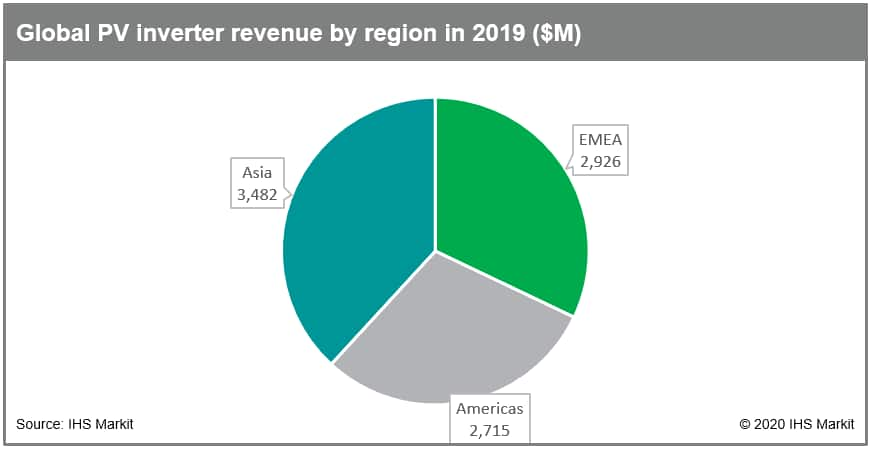
Figure 1: Global PV inverter revenue by region in 2019
($M)
Suppliers are pushing the limits of PV inverter technology
Several key technology trends offer opportunities for PV inverter suppliers to compete more aggressively in a growing industry. For example, suppliers continue to release larger inverters, particularly three-phase string and central inverters for utility-scale installations. Over the last few years, three-phase string inverter suppliers have worked hard to educate customers on the merits of a distributed architecture for large PV systems. Overall, these suppliers have succeeded as the penetration rate of string inverters has steadily increased especially in large commercial and small utility-scale installations. Recently, suppliers have released string inverters exceeding 200 kW as they begin to compete for larger system sizes and bid for highly price competitive projects.
Similarly, the same trend is influencing central inverter suppliers with leading suppliers releasing larger average sizes. Shipments of larger stand-alone central inverters between 3-4 MW increased 67% to reach 15.5 GW to account for over a third of central inverter shipments globally in 2019. IHS Markit expects larger central inverter shipments to increase in the next five years as central inverter suppliers aim to compete more aggressively on a dollar-per-watt basis and to defend against the encroachment of larger string inverters in utility-scale installations. As suppliers continue to push the limits of PV inverter power, they turn to new materials and software that can help them make the next leap in technology. For example, suppliers are carefully monitoring silicon carbide prices, which hold the potential for inverter designers to build even more efficient and power-dense PV inverters. Meanwhile, suppliers across the entire balance of systems are waiting for cues on a shift towards even higher voltages, particularly in utility-scale installations where the standard has rapidly become 1500V.
Cybersecurity, AI and enhanced software features increasingly important
Advanced software and grid features such as voltage control, frequency control and reactive power at night have become the prerequisite for inverter suppliers to be selected by system owners to futureproof their solar investments. Advanced software requirements include performing operation and component tests in real time such as IV curve diagnostics are now increasingly commonplace and provided by leading suppliers such as Huawei and Sungrow. As inverters are considered the brains of the PV plant, advancements including artificial intelligence and cybersecurity are becoming center stage as suppliers aim to add increasingly adaptability and protection to solar assets. PV inverter suppliers recognize that increasingly PV inverters will interact with the grid from a residential level up to utility-scale system. As a result, it will be incumbent on suppliers to implement the highest levels of cybersecurity to ensure to utilities and homeowners are protected to the highest standards against any malicious attacks to their energy systems.
Residential inverter market booms in 2019
The residential PV inverter market was the fastest growing system type, increasing over 50% in 2019. Solar inverter suppliers who offered single-phase and three-phase <10kW inverters in their portfolio in 2019 were able to take advantage of this market opportunity. Leading module level power electronic (MLPE) suppliers such as SolarEdge and Enphase as well as single-phase suppliers such as SMA, Growatt and Ginlong increased shipments to this segment. Key residential markets such as China, United States, Netherlands, Japan and Australia were instrumental in aiding the growth of global residential installations. PV inverter suppliers continued to innovate in this segment with aesthetically designed products built to be lighter, smaller, more power dense, and with new safety features.
Chinese suppliers accelerate internationalization to increase growth opportunities
PV inverter demand decreased for the second year in a row in China in 2019 due to declining installations. Although China remains the largest solar market in the world, Chinese suppliers, which had previously enjoyed huge growth by supplying their domestic market, have set their sights on international markets to help limit the impact of smaller domestic market and offset any revenue loss due to continued price pressure. Chinese-based suppliers have increased their international market share by seven percentage points to 38% in 2019.
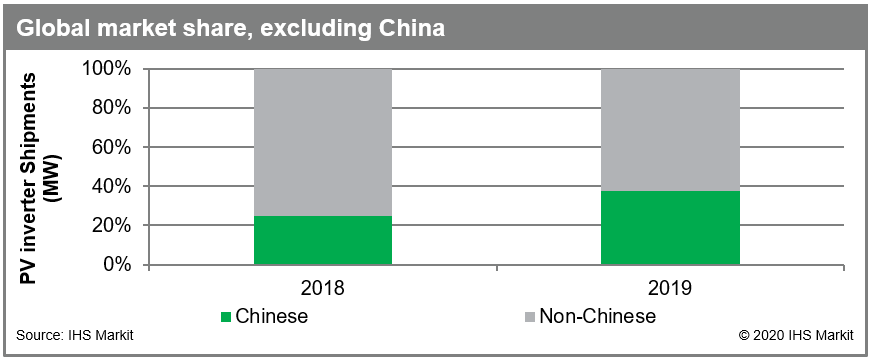
Figure 2: Global market share, excluding China
In particular, they have quickly expanded their presence across Europe, India, Southeast Asia and Latin America. Chinese suppliers continue to make significant investments to rapidly update their products to meet local grid and technical requirements and set up local sales and services offices. To help fuel this expansion, some Chinese suppliers such as Ginlong and Sineng have turned to investors by issuing shares in an IPO. The result is an increase in diversity of the competitive landscape in these regions. Strong growth in new installations in several major solar markets have benefited all suppliers, including key incumbent suppliers such as SMA, which has maintained a longstanding foothold in its home market in Germany and across Europe. Another example is Power Electronics, based in Spain, which maintains its leading position in its home market while achieving a dominant position in capturing booming growth in utility-scale shipments in the United States.
Overall, a more diverse group of PV inverter suppliers will be competing against each other in markets all over the world across all system types, from residential to commercial to utility-scale installations. Short term, strong price pressure will help some suppliers defend or increase their market share. Long term, the industry may potentially see further consolidation either as suppliers win out and acquire even greater share, or as suppliers merge or are acquired to build complimentary product portfolios.
To learn more about the IHS Markit solar research, visit our PV Inverter Intelligence Service page.
Miguel de Jesus is a solar market analyst for the Clean Technology & Renewables team at IHS Markit.
Posted 06 July 2020.
This article was published by S&P Global Commodity Insights and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.