How big is the CCUS market for equipment supplier?
Equipment suppliers sizing the rapidly expanding CCUS market as visible projects to 2031 are estimated to have 314 MMt/y of CO2 captured or injected/stored.
Many suppliers and contractors that are operating within the oil and gas industry have experienced a bumpy ride after the heydays that ended in 2014. Since then, they have experienced that dropping caused by a volatile oil price. However, the low-carbon industry is generating new opportunities. CCUS is part of this. In 2022-31, there are 113 visible CCUS projects. Looking ahead, S&P Global expects the trend of increasing low-carbon activity to continue. How big is this market for equipment suppliers? S&P Global has assessed the market size for some of the main components used in the CCUS industry - absorbers, strippers, heat exchangers, and compressors.
The attention on CCUS is rising rapidly as stakeholder pressure to decarbonize the global industrial economy continues to grow. CCUS is of particular interest because it is scalable, it is based on mature technology from the gas processing industry, and it is currently the only viable option for materially reducing CO2 emissions from energy-intensive industrial processes such as cement manufacturing and hydrogen production. Historically, CCUS developments have been smaller in CO2 capacity, often related to pilot projects, while going into the future we are seeing a trend for substantially larger CCUS facilities with higher CO2 capacity throughput.
• In 2012-21, 81 completed projects encompassed a combined 43
MMt/y of CO2 captured or injected/stored. This translates to an
average of 0.5 MMt/y of CO2 capacity per project.
• In 2022-31, 113 visible projects combined will amount to 314
MMt/y of CO2 captured or injected/stored. This corresponds to an
average of 2.8 MMt/y of CO2 capacity per project.
Some projects will most likely be cancelled, and some new ones can be expected to be added However, when we look at the number of all visible projects planned to come onstream in 2012-21, only 26% of projects were canceled or suspended. This indicates that larger-capacity CCUS projects were shelved, while those that came onstream had small CO2 capacities.
Development of CCUS infrastructure drives demand for equipment and services. There are substantial differences between CCUS project types with large variations between sizes, designs and development dynamics. Our demand analysis of equipment required for CCUS projects is correlated with the projects' CO2 capacities. While historical demand figures give us a picture of installations on facilities that are in operation today, the forecast demand shows us the market potential for equipment related to all visible CCUS projects planned to come onstream in 2022-31. We expect delays and cancelations to some of these projects, and new projects will appear.
The potential accumulated spending on the selected equipment categories absorbers, strippers, heat exchangers and compressors in the CCUS projects has been valued at USD3.7 billion in 2022-31, compared with USD708 million estimated in 2012-21. Based on the current project schedules, the peak in equipment demand should occur in 2025-27, with annual spending estimated at about USD700 million. The requirement for heat exchangers will be most capital intensive because of their complexity and a large number of units to be installed across the CCUS value chain.
Wolf Midstream was the largest buyer with a 34% market share for
CCUS projects completed in 2012-21 in terms of total CO2 capacity
of projects, with its Alberta Carbon Trunk Line project in Canada
completed in 2020, totaling 14.6 MMt/y of CO2. However, Europe is
expected to generate the most demand for equipment in 2022-31 with
its 47% market share in total equipment capital spending.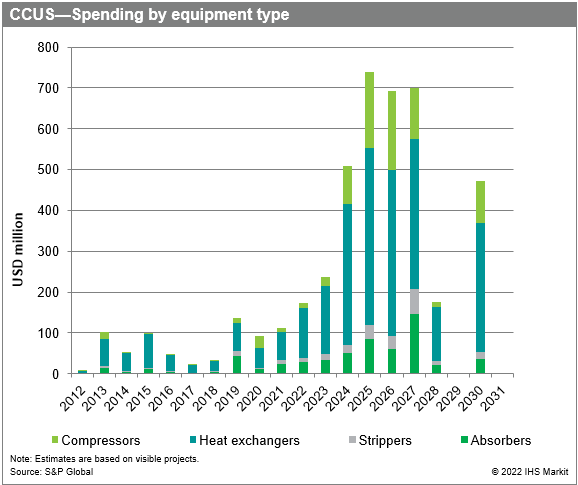
Heat exchangers require the most investments, accounting for 62% of
total spending for projects planned in 2022-31. This is because
heat exchangers are cost intensive owing to their complexity and
are widely used across the whole CCUS value chain.
Compressors are estimated to make up 20% of capital spending on equipment in CCUS projects in 2022-31, seeing that they are costly and complex machines, but their usage is limited to CO2 transport, injection for storage, or CO2 liquefaction processes.
Absorbers and strippers are the least capital intensive owing to their relatively smaller complexity and are estimated to account for a combined 18% of total spending in 2022-31. Their usage is limited to CO2 capture processes in the CCUS value chain.
CCUS provides a great opportunity for suppliers. In the text above, S&P Global has covered 4 equipment categories. However, this market provides opportunities for other players too, like EPC companies, pipeline, tube suppliers etc.
***
This is an extract from the CCUS supply chain review for more
information on this report contact James Blanchard or
subscribers to our Upstream Transformation Services can read the
full report "CCUS supply chain review" on
the S&P Global Commodity Insights Connect platform.
Want to learn more on this topic and access similar reports? Try
free access to the
Upstream Oil & Gas Hub to explore selected energy research,
analysis, and insights, in one integrated platform.
This article was published by S&P Global Commodity Insights and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.