Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.
Customer Logins
BLOG
Jan 28, 2021
Daily Global Market Summary - 28 January 2021
Most major US and European equity indices closed higher, while APAC was lower across the region. US government bonds closed lower and benchmark European bonds were mixed. European iTraxx and CDX-NA were close to unchanged across IG and high yield. Silver and copper closed higher, while the US dollar, oil, and gold were all lower on the day.
Americas
- Most US equity markets closed higher except for the Russell 2000 -0.1%; DJIA/S&P 500 +1.0% and Nasdaq +0.5%.
- 10yr US govt bonds closed +3bps/1.05% yield and 30yr bonds +3bps/1.81% yield.
- CDX-NAIG closed flat/55bps and CDX-NAHY -3bps/317bps.
- DXY US dollar index closed -0.2%/90.46.
- Gold closed -0.4%/$1,838 per ounce, silver +2.1%/$25.92 per ounce, and copper +0.6%/$3.58 per pound. Silver was as high at +6.5% on the day at 9:46am EST.
- Crude oil closed -1.0%/$52.34 per barrel.
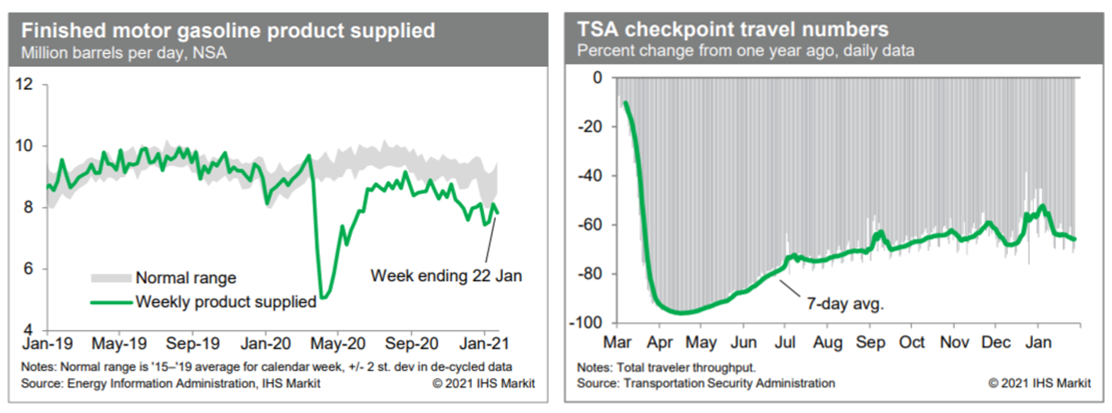
- Consumption of gasoline turned down last week, according to the
Energy Information Administration, remaining below a range that we
consider to be normal for this time of year. This indicates
continued weakness in internal mobility. Meanwhile, passenger
throughput at US airports has been trending lower in recent days to
levels similar to those prior to the holidays, indicating that the
boost to travel-related measures over the holidays was temporary.
(IHS Markit Economists Ben Herzon and Joel Prakken)
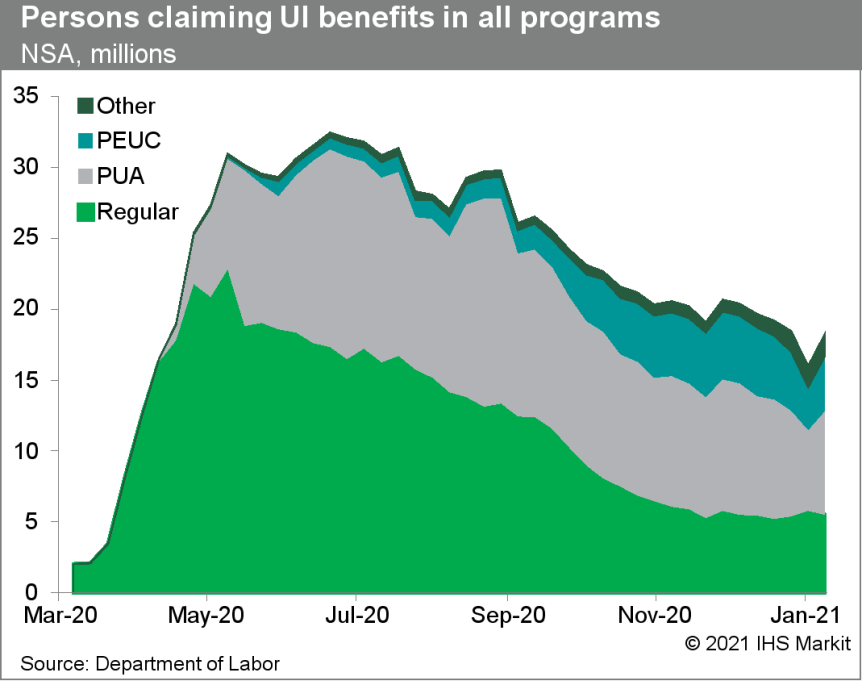
- US seasonally adjusted (SA) initial claims for unemployment
insurance fell by 67,000 to 847,000 in the week ended 23 January.
The not seasonally adjusted (NSA) tally of initial claims fell by
101,498 to 873,966. Despite falling last week, initial claims are
above levels seen in the past couple of months and remain at
historically high levels—the high during the Great Recession
was 665,000. (IHS Markit Economist Akshat Goel)
- Seasonally adjusted continuing claims (in regular state programs), which lag initial claims by a week, fell by 203,000 to 4,771,000 in the week ended 16 January. Prior to seasonal adjustment, continuing claims fell by 274,055 to 5,208,719. The insured unemployment rate edged down 0.1 percentage point to 3.4%.
- There were 426,856 unadjusted initial claims for Pandemic Unemployment Assistance (PUA) in the week ended 23 January. In the week ended 9 January, continuing claims for PUA rose by 1,626,796 to 7,334,193.
- In the week ended 9 January, continuing claims for Pandemic Emergency Unemployment Compensation (PEUC) rose by 836,596 to 3,863,548. With the latest extension to 24 weeks for PEUC, eligible recipients can receive up to 50 weeks of unemployment benefits between the regular state programs and PEUC.
- The Department of Labor provides the total number of claims for
benefits under all its programs with a two-week lag. In the week
ended 9 January, the unadjusted total rose by 2,293,495 to
18,282,090.
- US GDP grew at a 4.0% annual rate in the fourth quarter,
according to the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA)'s "advance"
estimate, as the economy continued to recover from last year's
sharp, pandemic-driven contraction. This was 1.0 percentage point
above our tracking estimate of 3.0% and left the level of GDP 2.5%
below the previous peak attained in the fourth quarter of 2019.
(IHS Markit Economists Ken Matheny, Michael Konidaris, and Lawrence
Nelson)
- Growth of personal consumption expenditures was firm (2.5%). Fixed investment posted strong gains driven by equipment investment (24.9%) and residential investment (33.5). The contribution of inventory investment to GDP growth declined sharply, from 6.6% to 1.0%, but remained positive. Net exports were a drag on GDP growth (down 1.5 percentage points), but less so than in the third quarter (down 3.2 percentage points).
- Relative to our final tracking estimate, personal consumption expenditures and nonresidential fixed investment rose more than we anticipated. Government consumption and gross investment declined less than we anticipated, driven by stronger-than-expected increases in defense and state and local spending. These upside surprises were only partially offset by lower-than-expected inventory investment and net exports.
- Waning of federal stimulus caused disposable personal income to fall 8.1%, as transfer payments fell nearly $0.6 trillion. This was partially offset by a $257 billion increase in labor compensation.
- Inflation moderated in the fourth quarter, although somewhat less than we expected. The GDP price index rose at a 2.0% rate, down from a 3.5% increase in the third quarter. The core personal consumption expenditures (PCE) index rose at a 1.4% rate in the fourth quarter, down from a 3.4% increase in the third quarter.
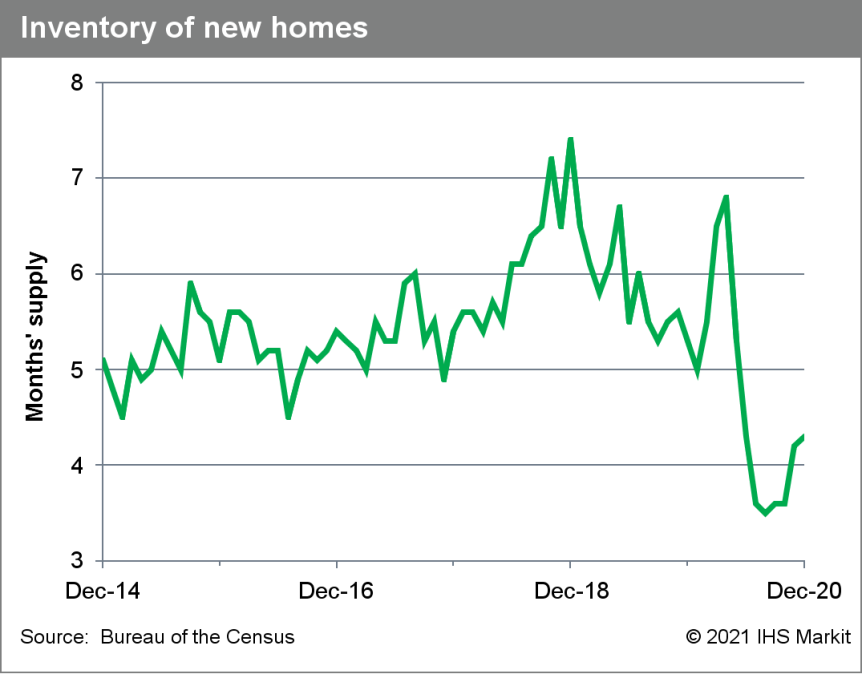
- This update is a first snapshot of US new home sales in the
fourth quarter and in 2020 overall. Following a 38.6% third-quarter
surge, new home sales tumbled 10.3% in the fourth quarter to an
873,000-unit seasonally adjusted annual rate. Sales fell in all
four regions. (IHS Markit Economist Patrick Newport)
- Annual sales increased 18.8% to 811,000, the highest total since 2006 despite the fourth-quarter slip. Sales last year climbed 24.2% in the Midwest, 21.2% in the Northeast, 18.9% in the West, and 17.6% in the South.
- In December, new home sales edged up 1.6% (±15.8%, not statistically significant) from November to a seasonally adjusted annual rate of 842,000. This was the first increase since July. Sales for the previous three months were revised down 8,000.
- The seasonally adjusted number of units for sale increased by 12,000 to 302,000; completed homes for sale were unchanged at 42,000; the months' supply of unsold homes inched up 0.1 month to 4.3 months.
- The average price increased 1.0% in 2020—despite strong demand and double-digit growth in existing home sale prices, new home prices have hardly budged since 2017.
- Are new home sales slowing? It is too soon to say. Single-family housing permits, arguably the most important housing market barometer, jumped 7.8% (±0.9%; statistically significant) in December—the eighth straight increase. Single-family permits were surging in all four regions at the end of last year. This suggests that the market for single-family homes still has legs.
- Today (28 January), the Census Bureau also released a full year
of single-family housing permits data at the state level. Fully 34
states saw double-digit growth in single-family permits last year;
in 10 states, permits grew by more than 20% and in 3 states by more
than 30%. Although new home sales are not available at the state
level, the state permits numbers suggest that in nearly every state
realtors specializing in new homes had a banner year.
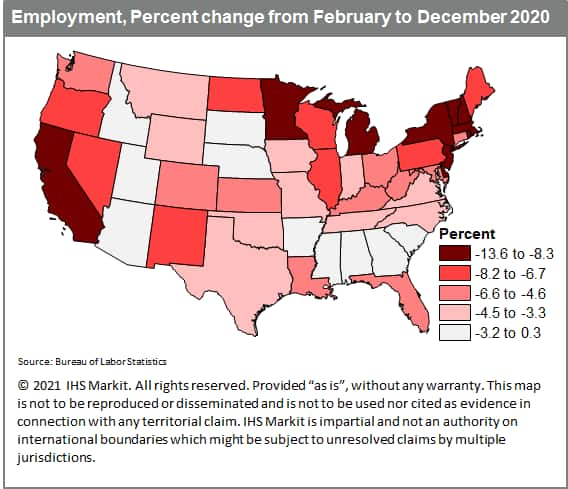
- Although total nonfarm payroll employment increased in 29
states in December 2020, in total states lost a net 26,500 jobs
from the previous month on a seasonally adjusted basis, according
to the most recent report from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics
(BLS). This was down from the gain of 400,100 jobs in November 2020
and is the first negative month since April 2020 when the
pandemic's economic impacts were at their worst. The December
numbers show a recovery continuing to lose steam, as COVID-19 case
numbers reached record levels across the nation. The leisure and
hospitality sector, specifically in food and accommodation
services, led the decline by a large magnitude, as many states
enacted a second round of shutdowns to quell the spread of the
virus. Retail and professional and business services, on the other
hand, saw solid payroll gains this month. A look at the percentage
change of total jobs from February to December 2020 shows which
state economies have fared the best or worst since the beginning of
the pandemic. States in the Northeast, specifically New York, New
Jersey, Massachusetts, Vermont, Rhode Island, and New Hampshire,
suffered the biggest early employment impacts from the coronavirus
outbreak and efforts to contain it. Meanwhile, tourism and
travel-reliant states such as Hawaii and Nevada, and heavily
goods-producing midwestern states such as Michigan also sustained
heavy blows. A good portion of manufacturing jobs have returned,
but businesses dependent upon travel and tourism face a much longer
road to recovery. In all these states, including those in the
Northeast, Hawaii, Nevada, and Michigan, December payrolls are at
least 8.0% below the February level. As we expected, the states
that fared the best in terms of employment losses are more sparsely
populated ones, with less dense metro areas and rural geographies
that naturally allow for social distancing, such as Idaho and Utah.
Meanwhile, states that experienced a more rapid rebound in May and
June, such as those in the South, are also closer to returning to
their pre-pandemic job levels. (IHS Markit Economist Steven
Frable)
- General Motors Co. GM has set a 2035 target date for phasing out gasoline- and diesel-powered vehicles from its showrooms globally, among the first major auto makers to put a timeline on transitioning to a fully electric lineup. GM's goal, disclosed in a social-media post Thursday from Chief Executive Mary Barra, would mark a striking transition from its current business model. Vehicles that run on fossil fuels and emit pollution account for roughly 98% of GM's sales today and all of its profit. (WSJ)
- Chinese tech company Baidu has received approval from the US state of California to test autonomous vehicles (AVs) in the state without a safety driver behind the wheel, reports Automotive News. The approval adds Baidu to a list of five other companies to which the Californian authorities have granted permission to test AVs on the state's public roads without a safety driver behind the wheel. Initially, California required safety drivers during testing of AVs. Reportedly, the authorities have approved 58 companies to test AVs in the state with a safety driver. The approval granted to Baidu is limited, allowing the company to operate three vehicles on specified streets of Sunnyvale, California. Baidu is planning to use Lincoln MKZ and Chrysler Pacifica vehicles during the testing. Baidu first announced plans to test AVs in the United States in 2016. Baidu carries out more-extensive AV testing in mainland China than in the US. However, the company's testing in the US signals an interest in participating in this market, likely with a robotaxi service, as it operates in Changsha, Beijing, and Cangzhou, Hebei province, China, which is open to the public but with a safety driver. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- Navistar is collaborating with General Motors (GM) and hydrogen
fuel provider OneH2 to develop and launch a hydrogen truck
ecosystem. Under the collaboration arrangement, GM is to supply
Hydrotec fuel-cell power cubes, and OneH2 is to provide hydrogen
production and fueling, according to a Navistar statement. (IHS
Markit AutoIntelligence's Stephanie Brinley)
- Navistar also states that JB Hunt Transport is to pilot the completed solution on dedicated routes. In a GM statement issued on its role in the collaboration arrangement, the automaker said Hydrotec fuel-cell power cubes are to be installed in Navistar International RH series trucks.
- The trucks will have two fuel-cell power cubes each. GM states that each power cube contains 300-plus hydrogen fuel cells and thermal and power management systems.
- The automaker says the Hydrotec fuel-cell power cubes are not designed specifically for the trucks. GM says that the compact and easy-to-package cubes can be used in a wide range of applications, "including marine, earth-moving and mining equipment, locomotives and power generators".
- The fuel-cell cubes provide 80 kilowatts of quiet and efficient net power and may be deployed in two or three units per vehicle for higher power, says the company.
- GM says that its proprietary technology increases fuel-cell and battery life and performance while optimizing cold-start performance; the cubes have low precious-metal content; and the cubes meet or exceed automotive and commercial safety standards.
- Navistar says it plans to start testing International RH fuel-cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) and begin a pilot program in 2022. The truck-maker says that it plans to make the first International RH FCEVs commercially available in 2024.
- Navistar says its target for the integrated solution is a range of 500-plus miles and a hydrogen fueling time of less than 15 minutes. Navistar says its fuel-cell electric trucks will feature better power density for short-range travel and better short-burst kW output than existing solutions, and per-mile costs that it expects to be comparable to diesel vehicles in some market segments.
- For the pilot program, OneH2 is to supply a hydrogen fueling solution. This will include hydrogen production, delivery, and storage. Navistar says that OneH2 plans to "kickstart substantial hydrogen heavy truck refueling infrastructure by incorporating more than 2,000 International RH Series FCEVs into existing fleet trucks in the near term".
- The latest announcement of an hydrogen FCEV program follows Navistar's announcement in November 2020 of a collaboration with Cummins on a hydrogen fuel-cell truck project funded by a US government program.
- Mexico's monthly index of economic activity (MIEA) expanded
0.9% in November 2020, down from 1.3% in October. This follows the
decelerating trend observed since July, after the initial (post
lockdown) rebound in June. (IHS Markit Economist Rafael Amiel)
- Seasonally adjusted data - from Mexico's National Institute of Statistics and Geography, INEGI - show that while the Mexican economy continues to recover, the pace of growth continues to slow down. The monthly index of economic activity (MIEA) expanded 0.9% in November, compared with October (month on month; m/m), when it had grown 1.3% m/m.
- Both the industry and services grew 1.1% m/m while agriculture was almost flat; there is still growth volatility among these three categories. Within the industry, manufacturing was flat, to some extent driven by the stabilization of exports, which have returned to pre-pandemic levels since September but did not significantly grow in the fourth quarter (Q4).
- On a separate report, INEGI informed that sales of non-financial services grew 2.6% m/m in November. On the annual comparison and using unadjusted data, sales of services were down 14.3% with respect to November 2019.
- The major driver of growth for Mexico's economy will be the US economy; Mexican exports of manufacturers will benefit from increased demand in the United States. IHS Markit projects total US imports will grow 15% in 2021.
- MIEA, which attempts to mirror GDP, suggests that the economy grew 2.7%-3.0% in Q4; this is higher than our estimate, so we will likely revise the (full year) 2020 decline from 9.0% to an 8.7% contraction.
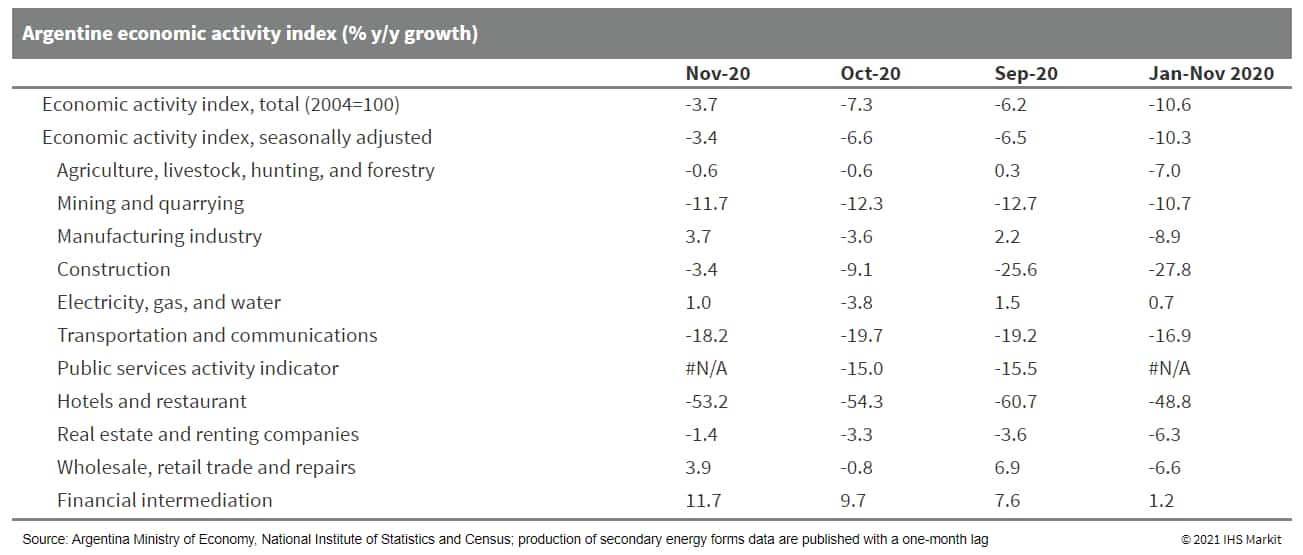
- Argentina's economic activity advanced by 1.4% month on month
(m/m) in seasonally adjusted terms, showing a further deceleration
in the recovery. The outlook remains complicated as the COVID-19
vaccination delays and infrastructure shortfalls create uncertainty
on the return to a less-restrictive mobility. (IHS Markit Economist
Paula Diosquez-Rice)
- The economic activity index decreased by 3.7% year on year (y/y) in November, while the seasonally adjusted data showed a 1.4% m/m increase during the month. For the first 11 months of 2020, the steep declines in March-May drove down the average to a 10.6% y/y decline.
- By sector, the economic activity index data showed mostly annual declines in November. There were steep declines in: the hospitality sector, which was down by 53.2% y/y; the transport and communication sector, which decreased by 18.2% y/y; the mining sector, which dropped by 11.7% y/y; and the construction sector, which fell by 3.4% y/y.
- Argentine real retail sales decreased by 1.1% y/y in supermarkets, but plunged by almost 46.7% y/y in shopping centers in November, as these were still being affected by the activity restrictions imposed by local governments. In terms of supermarket sales, less than 5.4% were online purchases; the main drivers of sales were electronic items and appliances, fresh produce, meats, and pantry dry goods.
- Customs trade imports increased in December 2020 compared with
December 2019 - led by the increase in capital goods and capital
goods parts imports. On the export side, a total decrease in value
by 34.1% y/y in December 2020 was due to a 33.8% y/y decrease in
volume and a 0.4% y/y decrease in prices. This slump was driven by
the decline in agricultural products, manufactured goods of
agriculture origin, and manufactured goods.
Europe/Middle East/Africa
- Most European equity markets closed higher except for -0.6%; Italy +1.2%, Spain +1.0%, France +0.9%, and Germany +0.3%.
- 10yr European govt bonds closed mixed; Italy -1bp, Spain flat, France/Germany +1bp, and UK +2bps.
- iTraxx-Europe closed flat/52bps and iTraxx-Xover -1bp/268bps.
- Brent crude closed -0.8%/$55.10 per barrel.
- Passenger car production in the United Kingdom slumped by 29.3% year on year (y/y) during 2020. According to data published by the Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders (SMMT), output tumbled from 1,303,135 units to 920,928 units. Of total production last year, 749,038 units were designated for export, a decline of 29.1% y/y, and 171,890 units were for domestic sale, down by 30.4% y/y. However, during December registrations slid by 2.3% y/y to 71,403 units, as while those for export fell by 11.9% y/y to 54,618 units, the number of vehicles designated for sale within the country jumped by 51.3% y/y. According to the SMMT, commercial vehicle production also fell during 2020, declining by 15.5% y/y to 66,116 units. Of this total, the number of vehicles built for export was down by 17.8% y/y to 37,893 units and production for domestic sale contracted by 12.2% y/y to 28,223 units. Output of vehicles in this category was also down by 9.2% y/y to 6,638 units in December. The steep falls were to be expected following at least two months when manufacturing facilities in the country were closed during the first half of the year as a result of the COVID-19 virus pandemic, while for other sites it was far longer. This has led to the lowest passenger car production levels since 1984, while commercial vehicle production has been the lowest since 1933. However, Brexit uncertainty overhanging until late in the year will also have been a factor. Looking forward into 2021, IHS Markit forecasts that passenger car production will improve to over 1 million units as a degree of normality returns, although it will also be the year that Honda closes its Swindon facility. We also expect more improvements in the coming years, although the short-term peak is set to be under 1.2 million during 2023, a far cry from the 1.7 million units achieved during 2017. As for light commercial vehicle (LCV) production, IHS Markit sees a significant improvement during 2021, with output expanding 27% y/y. We also see LCV output reaching almost 100,000 units during 2023. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Ian Fletcher)
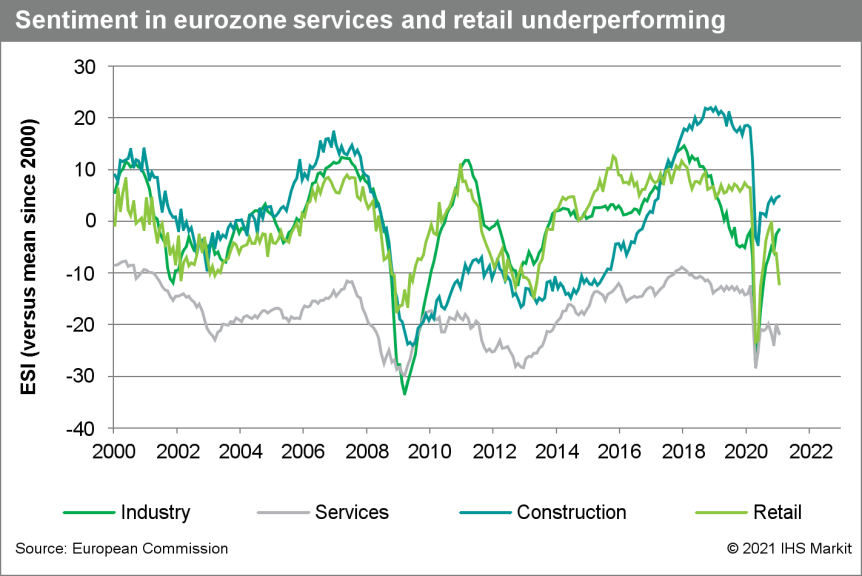
- More stringent and widespread COVID-19 virus containment
measures have driven weakness in the services and retail sectors,
while industrial resilience continues. (IHS Markit Economist Ken
Wattret)
- The "headline" economic sentiment indicator (ESI) for the eurozone has fallen less sharply than expected in January, by just under one point (to 91.5, well above Reuters' consensus of 89.5). December 2020's initial release has been revised up by two percentage points (to 92.4).
- Still, despite the upward surprises, January's ESI remains more than eight percentage points below its average since 2000 and over 12 points below its pre-COVID-19 level back in February 2020.
- Moreover, sentiment across sectors continues to show marked divergence, principally due to the differing impact of COVID-19 virus-related restrictions.
- Industrial sentiment continues its recent resilience, echoing the relatively strong performance already evident in IHS Markit's "flash" manufacturing PMIs.
- Industry accounts for the largest weight in the ESI (of 40%). At -5.9 in January, following a rise of around one point versus December 2020's level, industrial sentiment is now just marginally below its average since 2000.
- While economic conditions in the eurozone remain challenging as a result of the COVID-19 virus pandemic and its consequences, external demand has been supportive. Since June 2020's trough, the sub-index of export orders has risen by more than 25 points.
- In contrast, services sentiment has continued to struggle in January, with the index around 22 points below its average since 2000.
- Retail sentiment has plunged in January, meanwhile, by six
points, again primarily due to COVID-19 virus-related restrictions.
Following three straight declines, retail sentiment is now 12
points below its long-run average.
- Germany's Federal Statistical Office (FSO) has reported, based
on data from various regional states, that the country's national
consumer price index (CPI) has increased by 0.8% month on month
(m/m) in January, which compares with a decline of 0.6% m/m on
average for this month in recent years. (IHS Markit Economist Timo
Klein)
- The annual inflation rate has jumped from -0.3% in December 2020 to 1.0%. The EU-harmonised consumer price index (CPI) measure has even posted a reading of 1.4% m/m, its y/y rate thus increasing by an even larger margin from December's -0.7% to 1.6% y/y. This reflects the additional factor of a readjustment of weights every January (whereas national data weights only change every five years), which has led to major changes this time due to the impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) virus pandemic on consumer spending patterns.
- The detailed breakdown of the German national data will only be published with the final numbers on 10 February, but components are available, for instance, from the largest and most populous state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW). CPI inflation in this state is 0.9% m/m and 1.0% y/y, the latter rising from -0.4% in December.
- Energy prices in NRW have increased markedly by 5.4% m/m, pushing up their y/y rate from -5.5% to -1.6%. Owing to the VAT rise, all of the main other categories apart from alcohol/tobacco have posted a higher y/y rate than in December. Clothing/shoes, food, furniture/household goods, and "miscellaneous goods and services" are the other driving forces for inflation besides energy. It should be noted that due to lockdown conditions, the data for package tours and thus recreation and entertainment are statistically uncertain because of the dearth of relevant prices that could be obtained this month.
- NRW's core rate of inflation without food and energy has increased quite sharply from 0.3% y/y in December to 1.3% y/y in January. Most of this increase reflects the return to higher VAT rates, but it should be noted that this measure only declined by 0.6 percentage point in July 2020 when VAT was cut (from 1.3% to 0.7% nationwide). This suggests that supply shortages in certain areas of the economy - linked to the COVID-19 virus pandemic - are creating additional price pressures at the moment that are unrelated to seasonal effects.
- Service-sector inflation in NRW has increased from 0.9% to 1.3% y/y, while goods inflation has skyrocketed from -1.8% to 0.7% y/y.
- German inflation has clearly exceeded consensus expectations in January, returning above 1% in underlying terms and thus leaving deflation territory well behind. Furthermore, it should be remembered that the fact that VAT was only cut in July 2020 means that base effects related to this event will only show up in y/y rates during the second half of the year. Thus, headline inflation rates should exceed 2.5% temporarily in that period before falling back to around 2.0% in 2022. Core inflation, which we had expected to be at 1.0% or only slightly higher in January, now appears to be closer to 1.5% already.
- MAN Truck and Bus SE has agreed a program of what it describes as a 'socially responsible' reduction of 3,500 jobs from its German headcount across what it describes as all employment groups, according to a company statement. In its statement, MAN was keen to stress there would be, "No layoffs for operational reasons at the German locations of MAN Truck & Bus SE." The cuts are the central component of a series of measures the company is hoping will improve earnings by up EUR1.7 billion (USD2.1 billion). However, while there will be no operational redundancies at the German production locations, the future of its Austrian production location in Steyr remains under discussion and the executive board is still planning to close the Plauen site, although its future is still being discussed with employee representatives. MAN's reduction in headcount has long been desired by the company's management, but the program has been accelerated by two main factors that have affected the company in the last 12 months. Of course, the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) virus pandemic has had a significant negative impact on the European truck market, while Tostmann's appointment to replace MAN's former CEO Joachim Dress last July appeared a move to put an executive in place at MAN who had been successful in helping to generate significant savings at the VW passenger car brand in his previous role as that company's board member of production and logistics (see Germany: 22 July 2020: VW passenger cars appoints new production board member). In terms of the plan to boost profitability, broken down, Tostmann and his executive team plan to generate EUR450 million annually through additional sales efforts. Material costs are to be cut by around EUR700 million as a result of innovative co-operation with suppliers starting as early as the concept design phase for products. The company also aims to achieve an annual improvement in material overheads and personnel expenses of up to EUR550 million. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Tim Urquhart)
- According to the national statistical office (INE), Spain's
employment fell again during the fourth quarter of 2020, albeit at
a slower pace when compared to the previous quarter. (IHS Markit
Economist Raj Badiani)
- On an annual basis, total employment fell by 3.1% year on year (y/y), or by 0.62 million jobs to 19.3 million in the fourth quarter, after y/y falls of 3.5% in the third quarter and 6.1% in the second, which was the first drop since early 2014.
- This compares to gains of 1.1% y/y in early 2020, 2.3% in 2019 and 2.7% in 2018.
- A breakdown by economic activity reveals that services endured the sharpest job losses in the fourth quarter, down by 3.6% y/y (537,100 jobs) to 14.6 million. This is in line with the COVID-19-related restrictions targeting the hospitality, leisure and travel sectors.
- Meanwhile, industry employment was 2.5% lower y/y, implying 70,000 fewer jobs to stand at 2.7 million.
- Firms shed workers on temporary contracts, which decreased by 9.0% y/y or 0.4 million to 4.0 million during the fourth quarter, outpacing the loss of permanent jobs (down 1.7% y/y or 0.208 million). Spain has a high incidence of temporary employment, which reflects still dense job protection legislation for permanent workers.
- In addition, limited tourism activity during the Christmas and New Year period triggered widespread cancellation or non-renewal of many seasonal temporary contracts.
- The INE notes that workers suspended via the Temporary Suspension of Employment (ERTE) are classified as employed. The ERTE scheme allows firms to suspend employment, with workers able to apply for unemployment benefits during the time of their suspension. In addition, companies participating in the scheme cannot dismiss returning workers from the scheme for six months.
- The number of unemployed people increased by 16.5% y/y to stand at 3.72 million during the fourth quarter. Therefore, the unemployment rate increased to 16.1% at end-2020, up from 13.8% a year ago.
- The rise in the unemployment rate has been moderated by workers who are in the government's furlough scheme, who are not included as unemployed in this survey. Spain is using the ERTE employment protection scheme to limit the number of redundancies in the face of an enforced lockdown of the economy.
- With Spain facing the prospect of another double-dip recession in early 2021 amid an extended state of emergency across Spain to tackle rising COVID-19 infections, the labor market conditions are likely to remain under pressure.
- Spain has imposed a night-time curfew in response to a second spike in COVID-19 infections. The curfew came into force on 25 October 2020 and is in place between the hours of 23:00 and 06:00. This is a further blow to Spain's larger than average hospitality and accommodation sectors, which are already struggling to contain job losses and corporate insolvencies.
- The increased COVID-19 virus-related safety protocols are likely to remain in the next few months, with new COVID-19 infections rising again. Therefore, many consumer-facing services will have to operate well below full capacity, while high-street retailers will continue to experience lower than normal footfall.
- AkzoNobel says that today it submitted a binding proposal to
acquire Tikkurila, having completed due diligence on the company.
The proposal relates to a tender offer for all the issued and
outstanding shares of Tikkurila at an offer price of €31.25/share,
representing a total equity value of about €1.4 billion ($1.7
billion). A potential tender offer is subject to customary
conditions, and could be announced as soon as February, with the
transaction expected to be completed in 2021, AkzoNobel says. The
offer follows AkzoNobel's nonbinding proposal to acquire Tikkurila
on 18 January, which followed an offer by PPG Industries to buy
Tikkurila. (IHS Markit Chemical Advisory)
- The company notes that the binding proposal is conditional on AkzoNobel and Tikkurila entering into a combination agreement pursuant to which the Tikkurila board recommends AkzoNobel's tender offer, and obtaining an irrevocable undertaking from major Tikkurila shareholder Oras Invest to accept AkzoNobel's offer. In addition, it says that the binding proposal is not conditional on due diligence or approval by AkzoNobel's supervisory board, which has approved submission of the binding proposal.
- The completion of the potential tender offer remains subject to conditions such as reaching a 90% acceptance level, obtaining required regulatory approvals, no legislation or decision by a court or authority preventing the transaction, no material adverse change regarding Tikkurila, and the combination agreement, the Tikkurila board's recommendation, and the irrevocable undertaking from Oras Invest remaining in force, AkzoNobel says.
- AkzoNobel would reserve the right to waive any of the conditions for completion of the potential offer, it says. The company notes that there is no certainty that the binding proposal will eventually lead to a final agreement between AkzoNobel and Tikkurila.
- AkzoNobel says it does not hold any shares in Tikkurila. The company is being advised by HSBC and J.P. Morgan as financial advisers, and De Brauw Blackstone Westbroek and Roschier as legal advisers, it says.
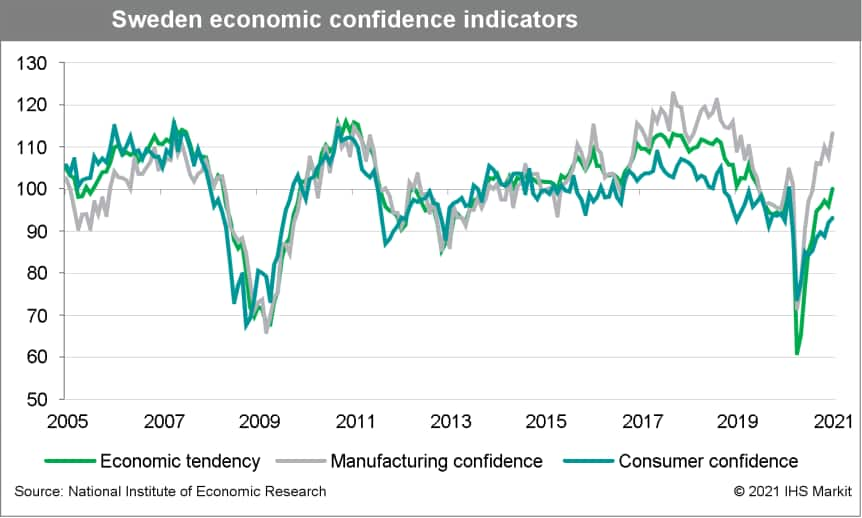
- Sweden's main confidence indicators shows manufacturing led the
improvement, as more optimistic expectations about the future were
the main contributor across most sectors. However, the outlook for
the first quarter of 2021 is challenging. (IHS Markit Economist
Daniel Kral)
- According to the Swedish National Institute of Economic Research (NIER), Sweden's economic tendency indicator improved to 100.0 in January, matching the 20-year average between 2000 and 2019, up from 95.9 in December.
- The improvement in January was broad-based but led by manufacturing, which at 113.3 was on a par with the levels in late 2018. All of the sub-components rose in January, but firms were most positive about their order books and expectations of higher production volumes in coming months.
- Consumer confidence rose by 1.1 points in January to 93.1, on a par with levels in late 2019, but still below the long-term average. Households are more optimistic about their personal finances in 12 months, slightly offset by their assessment of the current situation.
- Service-sector confidence rose by 3.6 points to 89.8, as current COVID-19-related restrictions in Sweden are less severe than in many other European economies. The improvement was broad-based and led by expectations of stronger demand in the coming months.
- The improvement is also reflected in the labor market with an improvement in firms' hiring plans and a decline in expectations of unemployment among households. This is complemented by labor force data from Statistics Sweden released today, which show an increase in employment in December and an unemployment rate of 8.7%.
- The latest data reinforces our view that Sweden avoided a
contraction in the fourth quarter of 2020, benefiting from a
positive carry-over into 2021. Based on our January baseline
forecast, Sweden is expected to maintain small but positive growth
in both quarters, in contrast with a much more pessimistic
Riksbank, which in its latest forecast from the end of November
expects a contraction in both quarters. A flash estimate of
Sweden's fourth-quarter 2020 GDP will be released on 2
February.
- Red wine occupies more than two-thirds of Russian alcoholic drink market volume and due to COVID travel restrictions, consumers will increasingly be interested in Russian wines. Wine is increasingly pushing out vodka from the list of preferences of Russians, who now mainly prefer red dry wine, according to the Roskachestvo's medium-term forecast on the development of the wine market. "In 2021, the trend of replacing spirits with wine in large cities of the country, where the wealthier consumer audience is located, will continue. This is a steady trend not only in Russia, but throughout the world," analysts said. Wine was in demand in 2020: if vodka, sales of which increased during the spring lockdown period, was also bought as an antibacterial disinfectant, wine was chosen for its quality. According to Roskachestvo's estimates, red wines occupy more than two-thirds of the total market volume. The share of rosé wines has grown to 4%, and light whites are also growing in popularity. Researchers predict that the average price of a quality bottle of wine in 2021 will grow from RUB300-500 (USD3.98-6.63) per 0.75 liter bottle to RUB400-600, and buyers will increasingly focus not only on their own experience, but also on the products' ratings, popular applications and opinions by critics. According to analysts, the most influential will be the recommendations of video bloggers. In addition, in 2021 on-site winery purchases will increasingly contribute to sales. "We would like to be optimists, but the dynamics of the incidence of Covid in Europe and the EU policy to restrict travel do not give hope for a full holiday season in Italy, Spain and other traditional 'wine countries'. A significant part of the tourist flow will remain within Russia, where the Crimea and the Kuban are the main winemaking regions," Roskchestvo said. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Jana Sutenko)
Asia-Pacific
- APAC equity markets closed lower; Hong Kong -2.6%, Mainland China/Australia -1.9%, South Korea -1.7%, Japan -1.5%, and India -1.1%.
- The China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC)
and the People's Bank of China, the central bank, jointly issued a
notice on 25 January of the granting of approval for the use of
equity-conversion bonds by two Chinese commercial banks, Zhejiang
Chouzhsou Commercial Bank and Ningbo Commerce Bank. According to
the Chinese-language-only notice, Ningbo Commerce Bank issued
CNY500 million (USD77 million) worth of such perpetual bonds with a
coupon of 4.8% on 20 January. (IHS Markit Banking Risk's Angus Lam)
- The notice states that these equity-conversion bonds will automatically convert into equities when a "risk event" is triggered, instead of the usual write-off process. This gives investors' "improved protection" by allowing them to "participate in the remaining asset allocation" process.
- A few events in China in recent months have heightened investors' risk aversion to investments. For example, unease has been created among investors by recent high-profile defaults of several state-owned Chinese corporations (see China: 18 December 2020: China's bond defaults: Impact on economy, banking sector, and state enterprises) and the bond write-off from the first Chinese bank default in nearly 20 years (see China: 16 November 2020: China's Baoshang Bank writes down CNY6.5-bil. tier-2 bond, likely limited contagion risk).
- According to data from China Central Depository & Clearing Co Ltd, over the 12 months to December 2020, investments in commercial banks' basic bonds increased 21% and investments in banks' tier-2 capital bonds (the largest proportion of commercial bank bonds) increased 16.5%. This suggests rising issuances of such bonds at a time of higher potential credit risks due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Overall, the development will likely increase further the demand for bank bonds, especially from smaller banks, which saw more than 20 mergers and reorganizations in 2020, as of August. Investors will feel more secure that they will not lose all their investment in the case of a default, which we judge as the meaning of a "risk event". Overall, IHS Markit continues to expect that a disorderly winding up of banks is unlikely, as this would create contagion risks and threaten overall financial-sector stability.
- Ford announced on 28 January that the Mustang Mach-E electric sport utility vehicle (SUV) will be manufactured in China by its Chinese joint venture (JV) Changan Ford. It will be available in the market later this year, according to a company statement. The Mustang Mach-E manufactured in China will measure 4,739 mm long, with a wheelbase of 2,984 mm. Ford has not announced the battery size, although it has said that it can deliver an estimated range of more than 600 km. With regards to technology content, the Mustang Mach-E will be able to provide automated driving functions with Ford's Co-Pilot 360 system. The model will also support firmware over-the-air (FOTA) updates on features like vehicle control and the infotainment system. The performance version of the Mach-E will be made available in China as well, and Ford said that it will also be produced locally. Powered by two electric motors, the performance GT version will be able to accelerate from 0-100km/h in less than four seconds. (IHS Markit AutoIntelligence's Abby Chun Tu)
- Baoneng Motor and its subsidiary Foresea Seven Swords have partnered with Aurora Mobile to develop intelligent vehicle solutions. Under this partnership, Aurora Mobile will offer its technical expertise to Baoneng Motor and Foresea Seven Swords to enhance their intelligent mobile transportation services. Aurora Mobile will also expand applications of its artificial intelligence (AI)-powered operational data analysis and insight to users' behavior in the automotive and Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) industries. The automotive industry is facing major changes with the introduction of automated vehicles, electrification of vehicles, and intelligent networks. Baoneng Motor aims to capture market share in these future technologies and considers research and development (R&D) linkages in the automotive industry chain as a top priority. In November 2020, the company established Foresea Seven Swords, an automotive software company designed to offer intelligent vehicle-related software and innovative business models. At the Auto China 2020 exhibition, Baoneng Motor launched the xEV platform, which is compatible with multiple power solutions. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- AutoX has launched a fully driverless robotaxi pilot program for the public in Shenzhen (China). Riders must sign up for the pilot service to hail robotaxi rides with no human attendant on board, reports Pandaily. AutoX has been testing driverless cars in Shenzhen since December 2020. The company has also received a permit to test its autonomous cars without a human safety driver in California (see United States: 20 July 2020: AutoX receives permit to test driverless cars in California). Last year, AutoX launched a robotaxi service for the public in Shanghai after conducting trials with signed-up users. (IHS Markit Automotive Mobility's Surabhi Rajpal)
- Japanese alternative meat company Next Meats has launched on the US stock market just days after concluding a joint development agreement with Taiwan's Hoya. Tokyo-based Next Meats this week went public on the American OTC Market and said it also hopes to be listed on the NASDAQ in the near future. The food tech venture company began product development in 2017 and was officially established in 2020, when it simultaneously started expanding overseas. The company has since established itself in Japan's alternative meat segment with a product range that includes Next Burgers, Next Gyudon, and the Next Yakiniku. Next Meat's growth has been supported by collaboration with Yakiniku Like, a Japanese barbecue chain restaurant. The company has also established a production site in Vietnam, and earlier this month signed a joint development agreement with Taiwan's Hoya, one of the world's largest alternative meat companies. Next Meat plans to start selling in Taiwan, Hong Kong, and Vietnam in March. Last December, Next Meats announced a partnership with Toyota Tsusho, a multi-market trading enterprise and affiliate of the Toyota Group Companies. The company says it will continue collaborating with universities and other venture companies to further research of plant-based proteins as well as microalgae and cultured meats. Ultimately, it says the aim is to replace all animal products by 2050. (IHS Markit Food and Agricultural Commodities' Max Green)
- As per IHS Markit's Commodities at Sea, Indian iron ore fines
and pellet exports during December 2020 stood at 4.6mt (up 10%
y/y). Shipments to China (Mainland) stood at 3.1mt or 67% of total
exports. During full 2020, Indian iron ore fines and pellet
shipments stood at 58mt (up 42% y/y) with the share of China
(Mainland) at 48mt (up 54% y/y). (IHS Markit Maritime and Trades'
Pranay Shukla)
- The Chinese government had increased infrastructure spending in the country which lead to a massive surge in the imports of iron ore and pellets. Australian iron ore miners were able to increase their exports to China; however, rain issues in Brazil and COVID-19 related lockdown in Peru reduced shipments from the two countries. During the period of surging international iron ore and pellets prices coupled with reduced Indian domestic steel production (until September 2020), there was a rush in exports of Indian ore cargoes since May 2020 which continued until the end of the year but at a reduced pace since October 2020.
- However, as per recent reports, there has been an acute shortage in the availability of iron ore material in the country due to the non-operationalization of the operating mines auctioned before March 2020. As per reports, iron ore production in the country during April-September 2020 dropped 31.5% y/y.
- Due to the shortage of steel-making raw materials in the country, the Indian steel Association requested the government to impose a six-month ban on iron ore exports from the country.
- Since COVID-19 related lockdown restrictions were lifted across the country domestic steel prices in the country started strengthening. Post-monsoons due to the restart of construction activities in the country HRC prices strengthened to INR 42,500-44,000/ton (USD 575-595, USD/INR~74). The strength in steel prices continued and by early January 2021, HRC prices hovered around INR 58,500- INR 60,500/ton (USD 790-820, USD/INR~74).
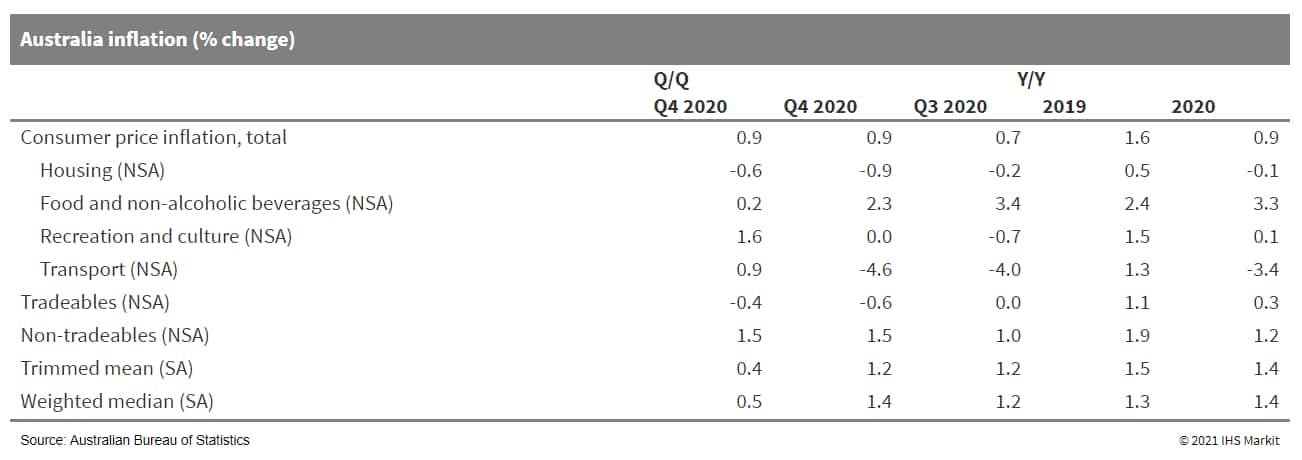
- According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS), the
greatest contributors to the uptick in inflation during the
December quarter included a 10.9% q/q rise in tobacco prices due to
annual excise tax increases, a 37.7% q/q increase in childcare
costs (recorded in the furnishings, household equipment, and
services component of the consumer price index), and a 2.5% q/q
increase in private healthcare premiums after a government-mandated
six month-freeze. (IHS Markit Economist Bree Neff)
- These price increases were offset by significant holiday price discounting at apparel retailers, and a 7.5% q/q decline in electricity prices caused by an electricity credit in Western Australia. Tradeables prices slipped during the quarter, mostly due to a 6.0% q/q fall in vegetable prices caused by easing domestic drought conditions, with some support from Australian dollar appreciation.
- The two core inflation measures - trimmed mean and weighted median - remain well below the RBA's 2-3% target range for headline inflation, indicating broader softness in price pressures.
- Australian inflation surprised on the upside from the one-off government measures in the fourth quarter. The impact of these one-off measures in q/q terms should fade significantly in the current (March) quarter release, but we anticipate a y/y spike in the June quarter of 2021 due to base effects from the economy recording deflation for that period in 2020. IHS Markit expects annual average inflation of 1.3-1.5% for 2021, partly because of that expected mid-year spike.
- Otherwise inflation should gradually pick up, as the domestic economy is operating with less stringent containment measures than in other countries due to actions by local governments to swiftly contain coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) virus outbreaks. Easing drought conditions will contain inflation, as will the continued strength of the Australian dollar, which will likely keep tradeables prices in deflation for the next one-to-two quarters at least.
- The RBA's first monetary policy board meeting of the year will
take place next week (2 February). However, its board will likely
wait until March or April to make adjustments to policy settings in
order to assess conditions and make decisions about how to proceed
with the AUD100-billion (USD77.2 billion) bond buying program,
which is set to expire in April. IHS Markit expects that inflation
will not become a significant topic for the RBA until the second
half of 2022.
S&P Global provides industry-leading data, software and technology platforms and managed services to tackle some of the most difficult challenges in financial markets. We help our customers better understand complicated markets, reduce risk, operate more efficiently and comply with financial regulation.
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
{"items" : [
{"name":"share","enabled":true,"desc":"<strong>Share</strong>","mobdesc":"Share","options":[ {"name":"facebook","url":"https://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?u=http%3a%2f%2fstage.www.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-28-january-2021.html","enabled":true},{"name":"twitter","url":"https://twitter.com/intent/tweet?url=http%3a%2f%2fstage.www.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-28-january-2021.html&text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+28+January+2021+%7c+S%26P+Global+","enabled":true},{"name":"linkedin","url":"https://www.linkedin.com/sharing/share-offsite/?url=http%3a%2f%2fstage.www.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-28-january-2021.html","enabled":true},{"name":"email","url":"?subject=Daily Global Market Summary - 28 January 2021 | S&P Global &body=http%3a%2f%2fstage.www.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-28-january-2021.html","enabled":true},{"name":"whatsapp","url":"https://api.whatsapp.com/send?text=Daily+Global+Market+Summary+-+28+January+2021+%7c+S%26P+Global+ http%3a%2f%2fstage.www.spglobal.com%2fmarketintelligence%2fen%2fmi%2fresearch-analysis%2fdaily-global-market-summary-28-january-2021.html","enabled":true}]}, {"name":"rtt","enabled":true,"mobdesc":"Top"}
]}