Key Strategic Issues Impacting the Global Ethylene Markets
Introduction
Historically, global demand for ethylene has grown at a multiple of
world GDP growth. However, the relationship between ethylene demand
growth and economic growth is becoming less straightforward. The
ethylene demand to GDP elasticity is being diluted by the
increasing influence of the technology and services sector on GDP
growth and the correspondingly lower impact of manufacturing. Also,
there has been a strong push toward sustainability and recycling,
so some ethylene demand has been replaced by recycled or natural
materials (paper, glass, etc.). This is resulting in lower
multiples to GDP growth, especially in developed countries. In
2019, ongoing trade tensions between the United States and China
have resulted in an overall slowdown in derivatives demand and a
shift in global trade flows. Prices of feedstocks were volatile in
2019 amid sanctions on Iranian crude oil, attacks on Saudi oil
production facilities, the upcoming 2020 implementation of a new
International Maritime Organization (IMO) fuel regulation, and
overall length in global LPG supply, all of which influence price
competitiveness and cracker feedslates. The 2019-2024 forecast
period projects ethylene demand growth at an average rate of 1.2
times GDP.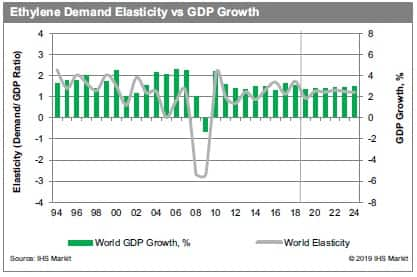
Global capacity addition has been uneven across global regions,
influenced by infrastructure and port facilities, feedstock
competitiveness, economic growth, and demand. Asia and the Middle
East have been leading new ethylene capacity addition in the past
decade, and Asia-particularly China-will continue to do so in the
next decade. The United States has also invested heavily in new
cracker projects in recent years due to an ethane feedstock
advantage with approximately 7 million metric tons (mt) of new
ethylene production facilities added in 2018-19. Capacity totaling
another 3.5 million mt is expected to come onstream in 2020.
Looking ahead, global capacity addition is expected to outpace
demand in the next few years. Consequently, IHS Markit forecasts
operating rates to drop in 2019-22; and recover from 2023
onward.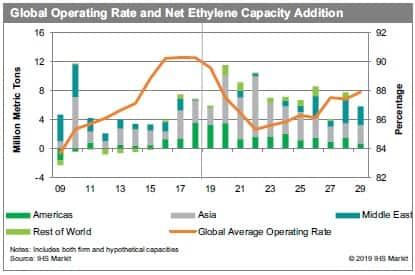
The emergence of lower-cost coal to olefins (CTO) and methanol to
olefins (MTO) technologies to produce light olefins starting from
around 2010 came at a time when crude oil and naphtha prices were
close to peak levels. As a result, in the years that followed, new
capacities in China were dominated by CTO and MTO, while interest
in traditional steam cracker projects was deferred due to weaker
project economics.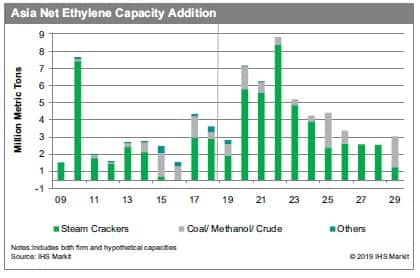
However, the tide is gradually shifting against MTO and CTO
technologies due to the current relatively low crude oil and
naphtha prices since the collapse at the end of 2014. The industry
also recognizes that both CTO and MTO technologies have their own
sets of challenges. CTO technologies are coming under increasing
scrutiny in China due to environmental reasons while MTO
technologies are uncompetitive due to high methanol feedstock
costs. As such, some new MTO and CTO projects were either delayed
or cancelled in China. Meanwhile, steam cracker projects are
regaining prominence due to both environmental and economic
advantages. In China and South Korea, most new cracker
expansions/investments allow for the use of both naphtha and LPG as
feedstocks. In China, there are also several gas crackers in
construction and planning phase amid competitive feedstock prices.
The economic advantage from cracking LPG compared with naphtha is
expected to last for the next few years as IHS Markit forecasts
that the length in the global LPG market will continue in next few
years whereas naphtha and gas oil supply is anticipated to tighten
due to implementation of the new IMO regulation. It is crucial for
Asian crackers to remain cost competitive, especially with capacity
growth outpacing demand, increased exports of competitive ethylene
and derivatives from integrated complexes in the United States, and
a slowdown in the global economy expected in the next few
years.
Trade
International trade of ethylene monomer will remain quite
limited overall compared with its derivatives owing to high freight
costs associated with transporting refrigerated liquids. However,
this is still necessary to maintain outlets for ethylene in regions
that have imbalances in production and consumption of ethylene, and
crackers operating at high rates due to high margins. In 2019, spot
cargoes from various origins-including the Middle East, Europe, and
Southeast Asia-have been shipped to Northeast Asia due to tight
supply in the region and workable pricing. Furthermore, sluggish
sales of key downstream polyethylene (PE) have resulted in several
integrated Asian producers offering spot ethylene monomer to
maintain high cracker operating rates. However, most of the
ethylene traded across international borders remains in the form of
derivative chemicals, including PE, ethylene glycol, styrene, and
vinyls (EDC) due to much lower transportation costs. IHS Markit
tracks the "net equivalent" trade volume globally, which is the
total amount of ethylene contained in the derivative trade. Shipped
as liquids or bulk solids, these ethylene derivatives are far less
expensive to transport than ethylene monomer.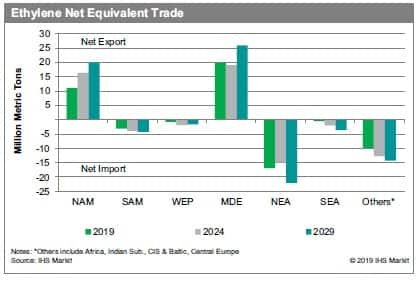
Despite slower economic growth and aggressive investments in new
ethylene/derivative capacities, China will continue to dominate
ethylene derivative imports. Ethylene equivalent exports from the
Middle East have increased rapidly as new capacities allow Middle
Eastern producers to increase PE and ethylene glycol exports to
Asia, mainly targeting China, although shipments are also going to
other regions. Exports of ethylene derivatives from the United
States to global markets are expected to increase over the forecast
period as new steam cracker and derivative capacities are brought
online in the next few years, taking advantage of the low-cost
ethane feed available. Meanwhile, exports of ethylene derivatives
from other parts of Asia (Southeast Asia, Japan, and South Korea)
will be impacted as these regional exporters become less
competitive compared with producers in other regions with feedstock
cost advantages.
Strategic Issues
There are other key strategic issues that, in the opinion of IHS
Markit, will have a significant impact on global ethylene markets
over the next 10 years. These are discussed widely and in greater
depth in the
2020 World Analysis- Ethylene.
2020 World Analysis - Ethylene
IHS Markit is pleased to present the
2020 World Analysis- Ethylene. This annual service provides our
clients with comprehensive analysis of and insight into the global
markets for ethylene. In addition to the electronic versions of the
study (Tableau, PDF files, and searchable HTML files on IHS Markit
Connect), clients can access the online capacity database, which is
updated daily, and the online supply and demand database, which is
updated once during the 12-month service period. Access to IHS
Markit consultants worldwide is also included in the 12-month
service period.