Southeast Asia’s Q3 power demand growth continues, with ongoing impacts from extreme weather, notably in Vietnam
S&P Global Commodity Insights recently released the Southeast Asia (SEA) power and renewable market briefing for the third quarter of 2023 (Q3 2023). The report discussed the power demand, supply, pricing, and major market events during the quarter, as well as the latest proposed or enacted policies and regulations. The report is now accessible on Connect.
The data from power market in figure below indicates a fluctuation in the year-over-year (YOY) power demand growth for Q3 2023 versus Q3 2022 in major SEA countries, including Vietnam, Malaysia, Singapore, and Thailand. There was a slower growth in Q3 power demand than in the previous quarter, ranging from -0.72% to 7.6%. The fluctuating YOY power demand trend suggests a moderate economy in the SEA region during Q3.
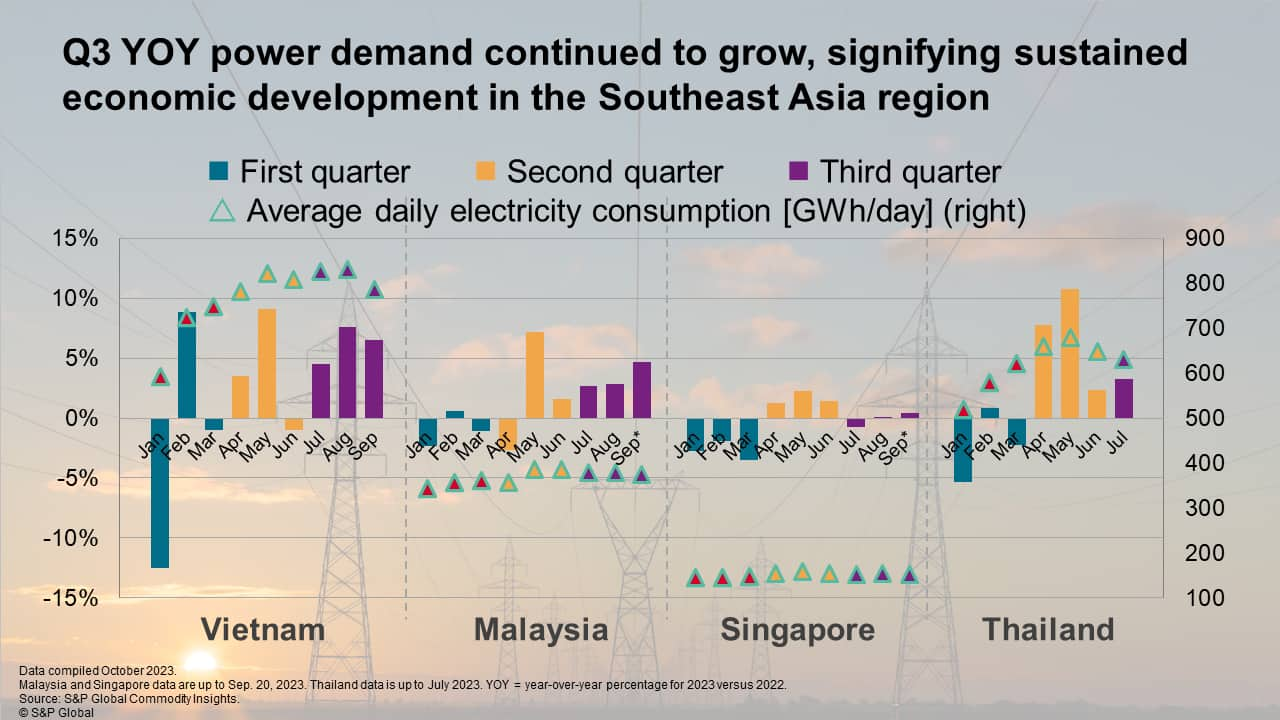
Vietnam continued to grapple with extreme weather, experiencing an average YOY growth of 6.2% YOY in Q3, significantly higher than Q2's 3.9% YOY. In addition, the country's power demand was also bolstered by the strong economic performance, and exhibited robust growth in July (4.5%), August (7.6%) and September (6.5%) which is also attributed to the country's robust economic growth. A similar trend was seen in the average daily electricity consumption for Q3 2023―high demand in July (826 GWh/day) and August (830 GWh/day) during persistent heatwaves, followed by a decline in September (787 GWh/day) due to flooding in North and Central regions.
Malaysia's power demand has consistently increased from 2.0% YOY in Q2 to 3.4% YOY in Q3. This can be attributed to the nation's stronger economic growth, particularly in the manufacturing sectors this year compared to the previous year. Rising global commodity prices for exports, particularly for energy and agricultural products in September, were the main driver of this growth. Amidst the ongoing dry weather, the average daily power consumption stayed consistent at 377 GWh/day in Q3 as opposed to 376 GWh/day in Q2.
As opposed to Vietnam and Malaysia, Singapore's power demand decreased to -0.1% YOY in Q3 from 1.6% YOY in Q2. This is attributed by the slowdown in advanced engineering and pharmaceutical exports markets, which has been made worse by the tightening global financial conditions. Nonetheless, owing to increased household demand during the prolonged dry season, the average daily electricity consumption in Q3 remained high at an average of 156 GWh/day as compared to 159 GWh/day in Q2.
Only July data is available for Thailand, which remained positive at 2.5% YOY. This is a notable decrease from the average growth of 7.0% YOY in Q2. The slowdown in July's power demand is owing to reduced global market demand for exports; after a robust increase in April and May, which was supported by a rebound in tourism-related business. In addition, July's average daily electricity consumption stood at 631 GWh/day due to rainy weather, significantly lower than the record high temperature in May, when the consumption rate reached 679 GWh/day.
The YOY power demand data indicates moderate economic growth in the SEA region, despite a decline in exports market. Months with declining trends were mostly influenced by the downturn in exports market, whereas the growing trends were supported by the recovery of industrial and commercial activities. However, it's evident that extreme weather events still affected the region's electricity consumption, although it's expected to diminish in Q4.
Learn more about our Asia Pacific energy market research and insights.
Choon Gek Khoo is a research analyst with the Gas, Power, and Climate Solutions team at S&P Global Commodity Insights focusing on data analytics for conventional energy in the Asia Pacific region, as well as analysis examining market and policy developments for Southeast Asian power and renewables markets.
Cecillia Zheng, associate director, is a key member of the Gas, Power, and Climate Solutions research and consulting team for Asia Pacific, leading Southeast Asian power market research.
Posted on 6 November 2023
This article was published by S&P Global Commodity Insights and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.