OECD Asia Power and Renewables Market Briefing, Q3 2023
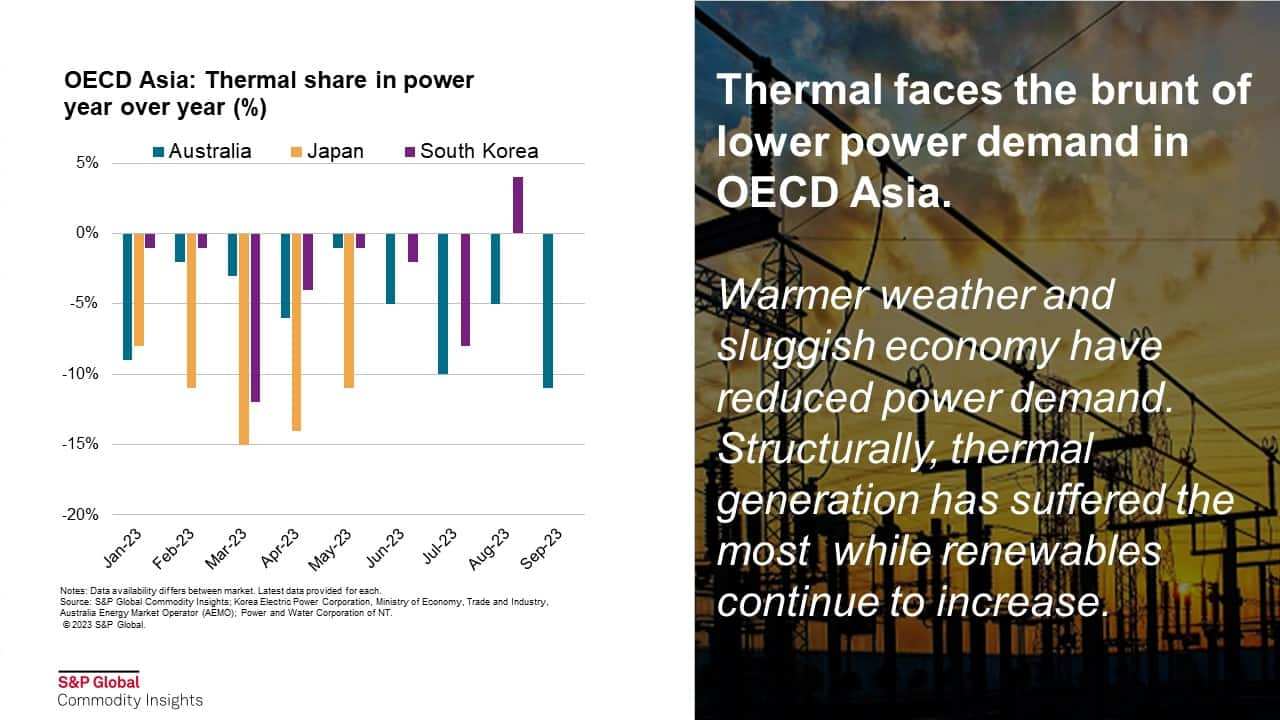
Power demand continues to decline year-on-year (YOY) in all 3 markets within OECD Asia (Australia, Japan and South Korea). Australia experienced its warmest winter on record (June-August), with national temperatures each month from June 2023 to September 2023 ranking in the top 10 warmest on record. The biggest decline was seen in Japan, with year to date (YTD) demand down -7.4% affected by a warmer winter, sluggish external demand suppressing industrial activity, and inflation continuing to affect the economy. Similar patterns were seen in South Korea, where lower external demand also suppressed overall power demand although to a lesser extent compared to the other two markets.
With demand down, thermal generation takes the brunt of the decrease as a mid-load power source - in Australia, the second-highest quarterly output from renewable (led by solar) reduced the thermal generation share to 62% during Q3 2023 — the second lowest on record. In Japan, YTD thermal generation was down 6.5%, while solar and wind were up 4% each. In South Korea, thermal generation was down 2%, while solar increased by 9% YOY.
Our new short-term forecast indicate power demand will be modest in both Japan and South Korea. In both markets, nuclear generation is expected to increase in 2024 with announced restarts in Japan and commissioning of a new reactor in South Korea. In Japan, three nuclear restarts will add 3GW to the nuclear capacity. In South Korea, one reactor with 1.4 GW capacity is scheduled to start during 2024. This will reduce the thermal gap, of which output from gas is expected to be impacted more than coal given historical fuel switching trends.
In this quarter, several new announcements and developments have been observed;
Australia
- On Oct. 1, 2023, Western Australia's Wholesale Electricity Market (WEM) commenced operating under updated market rules in the South West Interconnected System (SWIS). The reforms are designed to support the transition of a market historically dominated by state-owned gas and coal generation to a more competitive market with growing levels of renewables. The WEM Balancing Market is being replaced by a Real-Time Market, which includes a facility-level Security Constrained Economic Dispatch (SCED) on five-minute intervals — a move from state-owned Synergy dispatching its portfolio on 30-minute intervals. In addition, the Load Following Ancillary Service markets are replaced by five new frequency Essential System Service (ESS)Markets that will be co-optimized by the Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO) with energy in a new WEM dispatch engine. The ESS markets include a Regulation service (raise and lower) that requires delivery of the maximum quantity in five minutes, a Contingency Reserve (raise and lower) that requires automatic response in 400 ms, and a Rate of Change of Frequency Control Service to provide inertia.
Japan
- Regulated retail tariffs increased by approximately 9% to 14% from October 2023, as the government economic package was reduced to half of what was offered during the initial phase. The economic package was introduced in February 2023 to reduce the end-user impact of rising gas prices and reduce regulated power tariffs by ¥7/ kWh for residential prices and ¥3.5/kWh for industrial users on a volumetric basis. The impact from October is more marginal than initially expected. Based on S&P Global Commodity Insights' LNG price forecast, the regulated tariff will rise along with the winter LNG price hike, although the extent to which is still unknown given the current market dynamics.
- The offshore wind sector continues to face delays and decrease in project pipelines — in September 2023, the Goto Floating Wind Farm Consortium announced a two-year delay to its floating offshore wind project, sending further indications of the challenges Japan faces in achieving its 10-GW target by 2030. According to S&P Global's project database, approximately 9.9 GW of projects are currently in line to commence before 2030. Even for these projects, progress will need to be assessed over the next few years to evaluate the integrity of these volumes and dates.
South Korea
- On Oct .12, 2023, the competitive bidding for solar power fixed-price contracts for the second half of 2023 (H2 2023) was announced, with a bidding capacity of 1,000 MW and a ceiling price of 153,494 won/MWh for the mainland and 157,700 won/MWh for Jeju island, which is the same as the first half of 2023 (H1 2023). In this round, the carbon emission certification standards were strengthened with the reform of the solar module carbon verification system in January this year. Stricter emissions criteria, high Renewable Energy Certificate (REC) spot price and the same level ceiling price relative to the previous round are expected to deter participation in the Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS), as either the merchant market or corporate power purchase agreement (PPA) could yield comparable or higher returns.
- South Korea also announced a competitive bidding for wind power fixed-price contracts on Oct. 12 2023, with a total volume of 1,900 MW. The government sets a separate tender capacity for offshore and onshore wind as 1,500 MW and 400 MW, respectively, representing a significant increase compared with the previous year, partly reflecting the country's wind installation target of 19.3 GW by 2030. Some notable changes in this auction round include criteria for bid price evaluation, industrial and economic effects distribution, and system acceptability evaluation, which aim to address shortcomings from the previous round. Offshore wind power is expected to be the focus in this year's bidding, with about 2.5 GW of potential bidders that will be qualified to participate in the 1.5-GW bidding. If fully subscribed and awarded, this will lead to a significant jump from 99 MW of awarded capacity in the first wind auction last year.
Learn more about our Asia-Pacific energy research.
This article was published by S&P Global Commodity Insights and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.