Published February 2023
Hydrogen is produced in large quantities both as a principal product and as a by-product. Hydrogen producers may consume the product captively, sell it to end users, sell it to a company that specializes in marketing industrial gases, burn it for fuel, or vent it to the atmosphere. Hydrogen consumers may buy hydrogen from an industrial gas company or a by-product producer, use internally generated by-product hydrogen, or install a hydrogen plant on-site. In some cases, a company will generate crude by-product hydrogen that is purchased and purified by an industrial gas company and then sold back to the original generating company.
Growth in the hydrogen market is driven primarily by large-scale applications such as ammonia and methanol production, petroleum refining, and metals applications. Emerging use of hydrogen as energy carrier, either directly in fuel cells or as heating fuel, or indirectly in the production of renewable diesel (hydrotreated vegetable oils [HVO]), green ammonia, or green methanol, are emerging and fast-growing end-use segments.
The following pie chart shows world consumption of hydrogen:
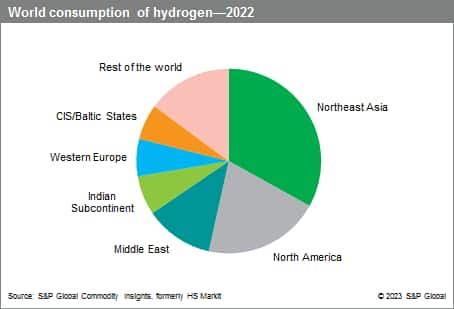
Most of all hydrogen produced today is still derived from fossil fuels, with natural gas being by far the most frequently used, followed by liquid hydrocarbons, coal, and electrolysis of water.
Global opportunities for hydrogen look strong in the forecast period. Production of methanol has been on the rise, especially in the United States, with lower natural gas prices providing an advantage. The ammonia market is also experiencing robust growth. Demand for distillate is steadily on the increase. Refineries are largevolume producers and consumers of hydrogen for distillate. In general, environmental regulations implemented in most industrialized countries result in increased hydrogen requirements at refineries for gasoline and diesel desulfurization because of increased demand for cleaner fuels and tighter engine manufacturer specifications.
Hydrogen is also expected to see a surge in consumption in the transportation sector as well as in other applications of hydrogen as an energy carrier, including the production of green ammonia and green methanol.
Overall global demand for hydrogen is expected to increase strongly during the next five years, primarily as a result of demand from petroleum refinery operations and the production of ammonia and methanol. Asia will continue to lead demand growth in line with the increasing growth of its domestic economies.
For more detailed information, see the table of contents, shown below.
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Hydrogen is the comprehensive and trusted guide for anyone seeking information on this industry. This latest report details global and regional information, including
Key benefits
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Hydrogen has been compiled using primary interviews with key suppliers and organizations, and leading representatives from the industry in combination with S&P Global’s unparalleled access to upstream and downstream market intelligence and expert insights into industry dynamics, trade, and economics.
This report can help you
- Identify trends and driving forces influencing chemical markets
- Forecast and plan for future demand
- Understand the impact of competing materials
- Identify and evaluate potential customers and competitors
- Evaluate producers
- Track changing prices and trade movements


















