Published September 2023
Ammonia is the basic building block of the world nitrogen industry; consumption of ammonia for nitrogen fertilizers accounts for nearly 80% of the world ammonia market. Nitrogen fertilizers are the most widely used fertilizers in the world, accounting for close to 60% of all fertilizers. With the exception of mainland China, where much of the ammonia is produced from coal gasification, most of the world’s ammonia is produced from natural gas.
The following pie chart shows world consumption of ammonia:
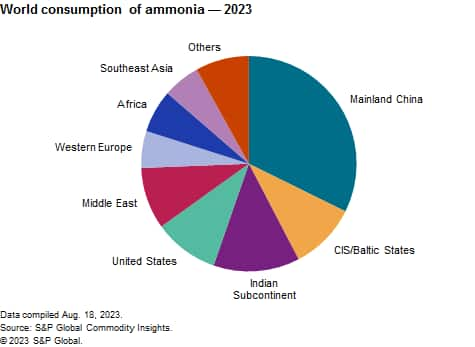
Ammonia is processed into downstream fertilizer products before being applied to the soil. These products include urea, ammonium nitrates, ammonium sulfate, ammonium phosphates and nitrogen solutions. Consumption of ammonia in industrial applications is projected to grow slightly faster than fertilizer use during the forecast period. Ammonia is used to produce ammonium nitrates that are used to make explosives (covered in the CEH Explosives and Blasting Agents report). It is also used in the production of acrylonitrile for acrylic fibers and plastics, hexamethylenediamine for nylon 66, caprolactam for nylon 6, isocyanates for polyurethanes and hydrazine and various amines and nitriles.
The shares of feedstocks such as naphtha and fuel oil are declining; natural gas is the preferred raw material for newer ammonia plants. During the forecast period, the share of natural gas is expected to increase. However, ammonia plants are expensive. Investment costs can exceed $1 billion, and plants can take up to three years to build.
During 2023–28, world apparent consumption of ammonia is forecast to increase at about 4.0% per year. The global ammonia supply/demand balance is expected to move toward a surplus, as future capacity additions will continue to outpace consumption. Ammonia capacity is increasing primarily in areas where the availability and cost of natural gas are lower, in particular the United States and the Middle East.
The advent of adopting net-zero emissions across the world is expected to increase the demand for ammonia in lowcarbon applications, with a rapid change in quantities consumed in the mid- to long term. Green ammonia is expected to play an important role in decarbonization existing applications and also to be used as bunker fuel and in the production of hydrogen and power.
For more detailed information, see the table of contents, shown below.
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook –Ammonia is the comprehensive and trusted guide for anyone seeking information on this industry. This latest report details global and regional information, including
Key benefits
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook –Ammonia has been compiled using primary interviews with key suppliers and organizations, and leading representatives from the industry in combination with S&P Global’s unparalleled access to upstream and downstream market intelligence and expert insights into industry dynamics, trade, and economics.
This report can help you:
- Identify trends and driving forces influencing chemical markets
- Forecast and plan for future demand
- Understand the impact of competing materials
- Identify and evaluate potential customers and competitors
- Evaluate producers
- Track changing prices and trade movements
- Analyze the impact of feedstocks, regulations, and other factors on chemical profitability

















