Published June 2023
Corrosion inhibitors are consumed primarily in three markets: water treatment, metal treatment and lubricants, and oil and gas production. Globally, water treatment is the largest market, with a share of about 45%, followed by metal treatment/lubricants/fuels, with about 30%. Oil and gas production accounts for the remaining corrosion inhibitor consumption, at around 25%. The global corrosion inhibitor market for water treatment is stable and will parallel the regional economic patterns, increasing at a low rate through 2028. Consumption for metal treatment is highly influenced by machinery manufacturing and operation. Demand for corrosion inhibitors in this application is expected to be sluggish in the next five years. Demand for corrosion inhibitors in oil and gas ultimately depends on the price of crude oil. It is expected that the crude oil price will be stable at a midlevel in the next five years. As a result, the corrosion inhibitor growth rate will not be high.
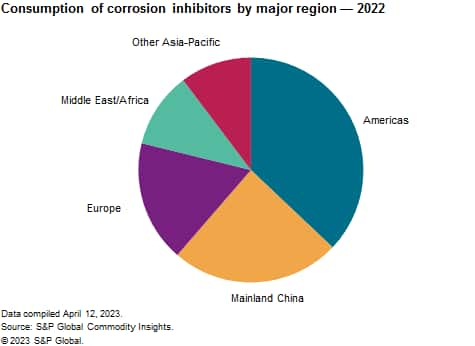
The following pie chart shows consumption of corrosion inhibitors in the major consuming regions:
Corrosion inhibitors can prevent system shutdowns and the loss of heat transfer, extend equipment life, help avoid product contamination and maintain appearance. Aside from corrosion inhibitors, other methods of combating corrosion include coatings and linings, cathodic protection and materials selection.
Most sales of corrosion inhibitors by their basic manufacturers are to service companies that formulate end-use products for the water treatment, lubricants and fuels, metal treatment (including metalworking fluids and rustpreventive oils), and oil and gas field production industries. The end-use products normally contain other functional components, as well as large volumes of solvents and dispersants. Although these service companies are more directly involved than basic manufacturers in the business of solving corrosion problems, the products and the technology of corrosion control are only a part, although an important one, of their overall business.
World consumption of corrosion inhibitors grew at less than 1% per year from 2019 to 2022, as markets were impacted by the COVID pandemic and the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Consumption is expected to grow at an average annual rate of 1%-2% during 2023–28. The relatively low growth rates projected for corrosion inhibitors reflect the high degree of maturity of most of the basic industries in which they are consumed. The replacement of steel by plastics, ceramics and corrosion-resistant alloys in the industries has also reduced demand for corrosion inhibitors in the industries. In addition, corrosion inhibitors are being used more efficiently by employing better monitoring and control techniques in order to minimize discharge in effluent streams and environmental impact.
One major market trend has been the positioning of the major Western water treatment companies, such as Ecolab, GE and Ashland, in mainland China. The other major trends in this business are related to regulatory and environmental concerns, which can result in the replacement of some product types by others that are either less toxic or perceived as less threatening to the environment. These issues can relate to the corrosion inhibitors themselves or to developments in the end-use market segment in which they are used.
For more detailed information, see the table of contents, shown below.
S&P Global’s Specialty Chemicals Update Program –Corrosion Inhibitors is the comprehensive and trusted guide for anyone seeking information on this industry. This latest report details global and regional information, including

Key benefits
S&P Global’s Specialty Chemicals Update Program –Corrosion Inhibitors has been compiled using primary interviews with key suppliers and organizations, and leading representatives from the industry in combination with S&P Global’s unparalleled access to upstream and downstream market intelligence and expert insights into industry dynamics, trade and economics.
This report can help you
- Identify the competitive environment and key players
- Assess key issues facing both suppliers and their end-use customers
- Understand industry integration strategies
- Keep abreast of industry structure changes, regulatory requirements, and other factors affecting profitability
- Identify new business opportunities and threats
- Follow important commercial developments
- Recognize trends and driving forces influencing specialty chemical markets

















