Published August 2022
Ammonium sulfate is used almost exclusively as a fertilizer material; minor amounts are used in nonfertilizer applications, including use as a cattle feed supplement, for several pharmaceutical applications, and for flameproofing, tanning, mining rare earth metals, food processing, fermentation, textile dyeing, and water treatment. In 2022, ammonium sulfate is used mainly (95% of world consumption) as a nitrogen fertilizer material and accounts for about 5.9% of the world nitrogen fertilizer market. Industrial use of ammonium sulfate accounts for only about 5% of world consumption.
World consumption of ammonium sulfate is concentrated in Southeast Asia and Oceania, Central and South America, mainland China, Western Europe, and the United States.
The following pie chart shows world consumption of ammonium sulfate:
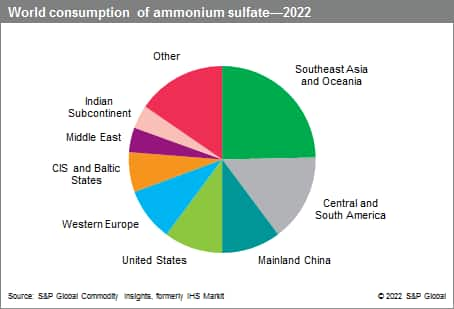
In general, the industrialized regions account for most of the world’s ammonium sulfate capacity, but mainland China has been the largest producer since 2012, followed by the United States and Western Europe. Because much of ammonium sulfate is produced involuntarily as a by-product or coproduct, the volume of production is influenced more by general industrial output levels than by fertilizer demand. As a result, the major capacity growth during 2012–22 occurred in mainland China, and mainland China is projected to account for the major gain during the forecast period, but at a slower rate.
Ammonium sulfate has a high sulfur content in the sulfate form, making it readily absorbable by plants. It has a low pH, making it suitable for alkaline soils. As a nitrogenous fertilizer, it competes with urea, ammonium phosphates, and ammonium nitrate. Sulfur has become increasingly recognized as an essential nutrient for plant growth since it supports the synthesis of amino acids, proteins, enzymes, vitamins, and chlorophyll. It has been found to be beneficial to a variety of crops, including canola, alfalfa, corn, potatoes, rice, vegetables, and wheat.
There are no serious environmental concerns involved with the use of ammonium sulfate as a fertilizer material. However, environmental concern does play an important role in the ammonium sulfate industry; a significant portion of the world’s ammonium sulfate production is the direct result of the necessity to remove SO2 from stack gases at various metal smelting and refining operations in order to conform to government regulations on SO2 emissions. A large potential source of additional by-product ammonium sulfate production is SO2 recovery from coal-fired electrical generating stations.
For more detailed information, see the table of contents, shown below.
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Ammonium Sulfate is the comprehensive and trusted guide for anyone seeking information on this industry. This latest report details global and regional information, including
Key Benefits
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Ammonium Sulfate has been compiled using primary interviews with key suppliers and organizations, and leading representatives from the industry in combination with S&P Global’s unparalleled access to upstream and downstream market intelligence and expert insights into industry dynamics, trade, and economics.
This report can help you
- Identify trends and driving forces influencing chemical markets
- Forecast and plan for future demand
- Understand the impact of competing materials
- Identify and evaluate potential customers and competitors
- Evaluate producers
- Track changing prices and trade movements
- Analyze the impact of feedstocks, regulations, and other factors on chemical profitability

















