Published December 2022
Mixed xylenes are the second-most-important aromatic product in terms of world consumption for chemical manufacturing, ranking behind benzene but ahead of toluene. The term mixed xylenes refers to the equilibrium mixture of four isomers with the same C8H10 chemical formula—para-xylene, ortho-xylene, meta-xylene, and ethylbenzene. Mixed xylenes are produced by several methods but petroleum is by far the major source; however, large volumes of the mixed xylenes produced during petroleum refining are not isolated but rather left in the refinery stream for use in the gasoline pool as an octane value enhancer. This application is not captured in this report; however, mixed xylenes markets can be greatly influenced by this alternative use.
Mixed xylenes are produced by several methods but petroleum is the major source. para-Xylene is the most widely used of the three xylene isomers. The major application for para-xylene is, by far, the production of purified terephthalic acid (PTA), which itself is used almost exclusively for the production of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) polymer for the manufacture of polyester fibers, PET solid-state resins, and PET film. The past 15 years have seen substantial investment in mixed xylenes capacity, primarily for use in para-xylene. These investments have been located mainly in Northeast Asia, which has a well-developed, integrated polyester industry as well as access to raw materials. Asian polyester producers have moved to back-integrate their business into purified terephthalic acid, para-xylene, and mixed xylenes to improve their cost-competitiveness.
Asia, with its large population, growing demand for polyester fiber (fibers, fabrics, and floor coverings) and polyester resins (beverage containers), and corresponding growth in the polyester industry, is solidifying its position as the center of influence for the mixed xylenes market.
The following pie chart shows world consumption of mixed xylenes:
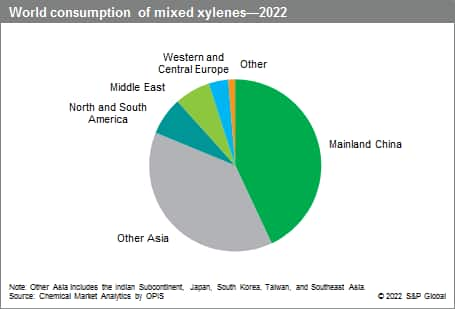
In the next five years, mixed xylenes capacity is expected to increase further, driven primarily by new investments in mainland China, and to some extent Southeast Asia and India. Consumption will also pursue its expansion, driven by incremental para-xylene requirements. In the long run, changes in fuel consumption are projected to modify the mixed xylenes production pattern; the industry will have to adapt to make up for the shortfall in reformate production as the world gradually transitions to greener energies.
Mixed xylenes trade is limited, accounting for 4% of global production in 2022; many producers are forwardintegrated into the production of isomers, therefore structurally limiting the merchant market. Northeast Asia drives global trade as both the largest importer and largest exporter, with the majority of trade being interregional, with Japan and South Korea exporting to mainland China.
For more detailed information, see the table of contents, shown below.
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook - Mixed Xylenes is the comprehensive and trusted guide for anyone seeking information on this industry. This latest report details global and regional information, including

Key benefits
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook - Mixed Xylenes has been compiled using primary interviews with key suppliers and organizations, and leading representatives from the industry in combination with S&P Global’s unparalleled access to upstream and downstream market intelligence and expert insights into industry dynamics, trade, and economics.
This report can help you
- Identify trends and driving forces influencing chemical markets
- Forecast and plan for future demand
- Understand the impact of competing materials
- Identify and evaluate potential customers and competitors
- Evaluate producers
- Track changing prices and trade movements
- Analyze the impact of feedstocks, regulations, and other factors on chemical profitability

















